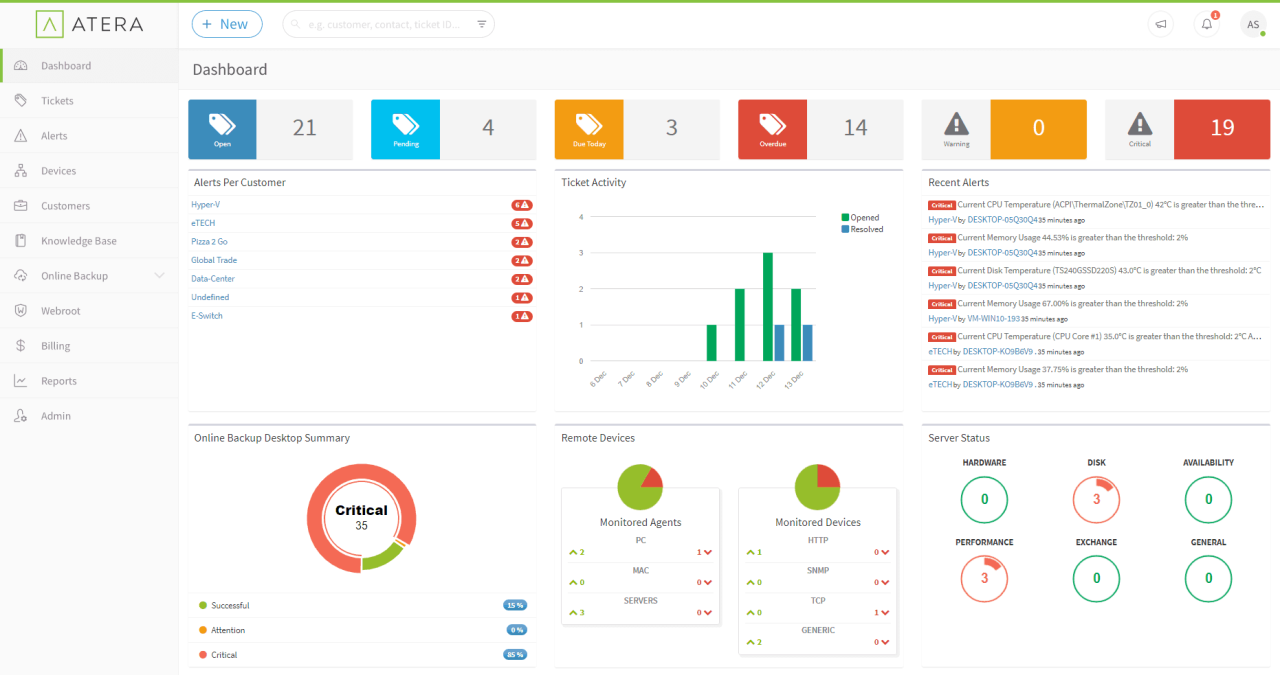
RMM management, or Remote Monitoring and Management, is a powerful tool for IT professionals looking to simplify and enhance their infrastructure management. This technology allows for remote monitoring and control of devices, automating tasks, and providing proactive security measures, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
Table of Contents
By leveraging RMM solutions, businesses can gain valuable insights into the health and performance of their IT systems. Real-time monitoring capabilities enable early detection of issues, allowing for prompt resolution before they escalate into major problems. Moreover, automation features free up valuable IT resources, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives rather than mundane tasks.
What is RMM Management?
RMM management, short for Remote Monitoring and Management, is a powerful suite of tools that enables IT professionals to remotely monitor and manage computer systems and networks. RMM solutions provide a centralized platform for managing endpoints, servers, and other devices, streamlining IT operations and enhancing overall efficiency.
Core Functionalities of RMM
RMM solutions offer a wide range of functionalities, encompassing key aspects of IT infrastructure management.
- Remote Monitoring: RMM tools continuously monitor endpoints for performance metrics, security threats, and system health. They collect data on CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and other critical parameters, providing real-time insights into device performance.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM solutions automate the process of installing software updates and security patches, ensuring that systems are always up-to-date and protected against vulnerabilities. This eliminates manual intervention and reduces the risk of security breaches.
- Remote Control and Management: RMM tools empower IT professionals to remotely access and control endpoints, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other administrative tasks without physically being present at the device location.
- Asset Management: RMM solutions provide a comprehensive inventory of all managed devices, including hardware and software details. This information is crucial for efficient asset management, software licensing compliance, and capacity planning.
- Security Management: RMM solutions play a vital role in bolstering security by detecting and mitigating threats, such as malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access attempts. They provide real-time threat monitoring, endpoint security configuration, and vulnerability scanning.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM solutions generate detailed reports on system performance, security events, and other critical metrics. These reports provide valuable insights into IT infrastructure health, allowing IT teams to identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and make data-driven decisions.
Role of RMM in IT Infrastructure Management
RMM solutions are essential for modern IT infrastructure management, playing a pivotal role in:
- Streamlining IT Operations: RMM tools automate repetitive tasks, such as patch management, software deployment, and system updates, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improving Efficiency and Productivity: By automating tasks and providing a centralized platform for managing endpoints, RMM solutions enhance IT efficiency and productivity, leading to faster resolution of issues and improved overall system performance.
- Enhancing Security Posture: RMM tools actively monitor for security threats, apply security patches, and enforce security policies, strengthening the overall security posture of the IT infrastructure.
- Reducing Costs: RMM solutions help reduce costs by minimizing downtime, automating tasks, and eliminating the need for physical site visits.
- Improving User Experience: RMM solutions ensure that devices are running smoothly and securely, leading to a more reliable and user-friendly IT experience for end-users.
Benefits of Implementing an RMM Solution, Rmm management
Implementing an RMM solution offers numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes:
- Enhanced Security: RMM tools provide real-time threat monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and automated patch management, significantly enhancing the security posture of the IT infrastructure.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: RMM solutions streamline IT operations, automate repetitive tasks, and provide a centralized platform for managing endpoints, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Downtime: RMM tools proactively monitor systems for potential issues, allowing for early detection and resolution, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
- Lower IT Costs: RMM solutions reduce IT costs by automating tasks, minimizing downtime, and eliminating the need for physical site visits.
- Improved User Experience: RMM solutions ensure that devices are running smoothly and securely, leading to a more reliable and user-friendly IT experience for end-users.
- Enhanced Compliance: RMM solutions assist organizations in meeting compliance requirements by automating tasks, tracking system configurations, and generating reports for audits.
Benefits of RMM Management
RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) software offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to streamline IT operations, enhance security, and improve overall system performance. These benefits translate into tangible advantages for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, and achieve greater operational efficiency.
Impact on IT Efficiency and Operational Costs
RMM solutions empower IT teams to manage and monitor endpoints remotely, eliminating the need for on-site visits in many cases. This remote access significantly reduces the time and effort required for routine tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and troubleshooting.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM automates the process of identifying and deploying security patches across all managed devices, ensuring that systems are always up-to-date and protected against vulnerabilities. This eliminates the manual effort associated with patch management, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Streamlined Software Deployment: RMM simplifies the process of deploying software updates and applications to multiple endpoints simultaneously. This automation eliminates the need for manual installations on each device, saving valuable time and reducing the risk of errors.
- Reduced Help Desk Costs: RMM empowers IT teams to proactively identify and resolve issues before they escalate into major problems. This proactive approach significantly reduces the number of help desk tickets and associated support costs.
- Improved IT Staff Productivity: RMM automates many repetitive tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more complex and strategic initiatives. This improved productivity allows IT teams to deliver greater value to the business.
Selecting the Right RMM Solution
Choosing the right RMM platform is crucial for optimizing your IT operations and maximizing efficiency. The right solution should align with your specific needs, budget, and existing IT infrastructure.
Key Factors to Consider
Evaluating different RMM vendors and their offerings requires a comprehensive approach. Consider the following factors:
- Scalability: The chosen RMM solution should be able to adapt to your organization’s growth and changing needs. Look for platforms that offer flexible pricing plans and can scale to accommodate a growing number of devices and users.
- Features and Functionality: The ideal RMM platform should offer a comprehensive suite of features that meet your specific requirements. This may include remote access, patch management, endpoint security, software deployment, and reporting capabilities.
- User-friendliness: The RMM platform should be easy to use and navigate, even for non-technical users. A user-friendly interface simplifies tasks, reduces training time, and promotes efficient adoption within your team.
- Security: Security is paramount for any IT management solution. Choose an RMM platform with robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security updates.
- Support and Documentation: Reliable customer support and comprehensive documentation are essential for troubleshooting issues and maximizing the platform’s potential.
- Pricing: Consider the cost of the RMM solution, including licensing fees, support costs, and any additional modules or features.
RMM Vendor Evaluation Checklist
A structured approach to evaluating RMM vendors is crucial. Use the following checklist to compare different options:
- Features and Functionality: Review the available features and functionality, ensuring they align with your specific requirements.
- Pricing and Licensing: Compare pricing models, licensing fees, and any additional costs.
- Integration: Evaluate the platform’s integration capabilities with your existing IT infrastructure, including operating systems, software, and other tools.
- Security: Assess the platform’s security measures, including encryption, access controls, and security certifications.
- User Reviews and Testimonials: Read reviews and testimonials from other users to gain insights into the platform’s performance and user experience.
- Customer Support: Investigate the availability and responsiveness of customer support, including phone, email, and online resources.
- Free Trial: Take advantage of free trials to experience the platform firsthand and assess its suitability for your needs.
Compatibility and Integration
Compatibility and integration with your existing IT infrastructure are crucial considerations. The RMM platform should seamlessly integrate with your operating systems, software, and other tools to avoid conflicts and ensure smooth operation.
Example: If your organization uses Microsoft Active Directory for user management, the RMM platform should integrate with Active Directory to synchronize user accounts and permissions.
Implementing an RMM Solution

Successfully deploying and configuring an RMM platform is crucial for reaping its benefits. The implementation process involves a series of steps, from initial setup to ongoing maintenance, to ensure smooth operation and maximize the platform’s potential.
Onboarding Devices
Onboarding devices is the process of adding them to the RMM platform for management. This step involves installing the RMM agent on each device and configuring it to communicate with the central server.
- Agent Installation: The RMM agent is a software component that runs on each managed device. It collects data, executes tasks, and enables remote control. The agent can be installed through various methods, including:
- Manual Installation: The agent can be downloaded and installed manually on each device. This method is suitable for a small number of devices or when automated deployment is not feasible.
- Automated Deployment: The agent can be deployed automatically using tools like Active Directory Group Policy, scripting, or the RMM platform’s built-in deployment features. This method is efficient for large-scale deployments and ensures consistency across devices.
- Cloud-Based Deployment: Some RMM platforms offer cloud-based agent deployment, which eliminates the need for manual installation or server-side configuration. This method is convenient for managing devices across multiple locations.
- Agent Configuration: After installation, the agent needs to be configured to communicate with the RMM server. This typically involves specifying the server address, authentication credentials, and other settings. The agent configuration can be customized based on the specific needs of the managed device and the organization’s security policies.
Managing User Permissions
User permissions define the level of access and control each user has over the RMM platform and the managed devices. Effective permission management is essential for security and accountability.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC is a common approach for managing user permissions. It involves defining roles with specific permissions and assigning users to those roles. This approach ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks. For example, a help desk technician might have access to manage endpoints and run basic scripts, while a system administrator might have access to configure the RMM platform and manage user accounts.
- Granular Permissions: RMM platforms typically offer granular permissions that allow administrators to control specific actions, such as remote control, software installation, or data access. This level of granularity helps to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that only authorized users can perform critical tasks. For instance, an administrator can grant permission to a technician to install software on a specific set of devices but not to access sensitive data.
- Auditing and Reporting: RMM platforms often include features for auditing and reporting on user activity. These features can help track changes made to the platform and identify potential security breaches. For example, an administrator can review logs to see which users have accessed specific devices or made changes to the platform’s configuration.
Integrating RMM with Other IT Management Tools
Integrating RMM with other IT management tools can streamline workflows and provide a unified view of the IT infrastructure.
- Ticketing Systems: Integrating RMM with ticketing systems like Zendesk or ServiceNow allows technicians to access relevant device information and manage tickets directly within the RMM platform. This integration can improve efficiency and reduce the time it takes to resolve issues.
- Monitoring Tools: Integrating RMM with monitoring tools like Nagios or Prometheus provides a comprehensive view of device health and performance. This integration can help identify potential issues early and prevent downtime.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Integrating RMM with SIEM systems enables the correlation of security events from managed devices with other security data sources. This integration can improve threat detection and incident response capabilities.
RMM for Different IT Environments
RMM solutions are adaptable and can be customized to meet the specific needs of various IT environments, from small businesses to large enterprises. This flexibility allows organizations to leverage RMM for efficient IT management and support, regardless of their size or industry.
RMM for Small, Medium, and Large Enterprises
The specific requirements of RMM vary significantly depending on the size of the enterprise.
- Small Businesses: Small businesses often have limited IT resources and budgets. They require an RMM solution that is easy to use, affordable, and can be managed by a single IT administrator. Features like automated patching, remote access, and basic monitoring are essential for small businesses to ensure system stability and security.
- Medium Enterprises: Medium-sized businesses typically have more complex IT infrastructure and require more advanced RMM features. They may need to manage multiple locations, have a larger number of devices, and require more sophisticated reporting and analytics. Features like user management, asset tracking, and more comprehensive security tools are crucial for medium enterprises.
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises often have extensive IT infrastructure, diverse user populations, and stringent security requirements. They require a robust RMM solution that can handle a large volume of data, integrate with existing systems, and provide advanced automation and reporting capabilities. Features like service desk integration, compliance reporting, and advanced threat detection are essential for large enterprises.
RMM Tailored to Different Industries and Sectors
RMM can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries and sectors.
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations require RMM solutions that comply with HIPAA regulations and ensure the security of patient data. Features like data encryption, access control, and audit logging are essential for healthcare RMM solutions.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions require RMM solutions that comply with regulatory requirements such as PCI DSS and ensure the security of sensitive financial data. Features like vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and security event logging are critical for financial services RMM solutions.
- Education: Educational institutions require RMM solutions that can manage a large number of devices, provide remote access for students and faculty, and ensure compliance with educational regulations. Features like device management, remote learning support, and user authentication are essential for educational RMM solutions.
RMM in Cloud Environments
RMM solutions are increasingly being used to manage cloud environments.
- Cloud Monitoring and Management: RMM can be used to monitor and manage cloud resources, including virtual machines, containers, and cloud applications. This allows organizations to ensure the performance, availability, and security of their cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud Security: RMM can help organizations secure their cloud environments by providing features like vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and security event logging. This helps organizations identify and mitigate potential threats to their cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud Cost Optimization: RMM can help organizations optimize their cloud spending by providing insights into resource utilization and identifying areas for cost reduction. This can help organizations save money on their cloud infrastructure.
RMM for Remote Workforces
RMM solutions are essential for managing remote workforces.
- Remote Device Management: RMM can be used to manage remote devices, including laptops, desktops, and mobile devices. This allows organizations to ensure the security and compliance of remote devices.
- Remote Support and Troubleshooting: RMM provides remote access and support capabilities, allowing IT professionals to troubleshoot and resolve issues on remote devices. This helps organizations provide seamless support to their remote workforce.
- Remote Security: RMM can help organizations secure remote devices by providing features like endpoint protection, patch management, and data encryption. This helps organizations protect their data and systems from threats, even when employees are working remotely.
Automation and RMM
RMM solutions are designed to streamline and automate repetitive IT tasks, freeing up valuable time for IT professionals to focus on strategic initiatives. Automation within RMM encompasses a wide range of functionalities, from simple script execution to complex workflow orchestration.
Benefits of Automation with RMM
The implementation of automation within RMM brings numerous benefits to IT teams, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
- Reduced Manual Labor: Automating routine tasks like software patching, system updates, and security scans eliminates the need for manual intervention, reducing the workload on IT staff. This allows them to focus on more complex issues requiring their expertise.
- Improved Consistency and Accuracy: Automated tasks are executed with precision and consistency, minimizing human error. This ensures consistent application of IT policies and procedures, leading to a more stable and reliable IT environment.
- Increased Productivity: By automating repetitive tasks, IT teams can handle a larger volume of work with the same resources. This translates to increased productivity and efficiency, allowing them to manage a growing IT infrastructure more effectively.
- Enhanced Security: Automated security tasks like vulnerability scanning and malware detection can identify and mitigate security threats proactively, reducing the risk of breaches and data loss.
Examples of Automated Tasks
- Patch Management: RMM tools can automatically scan for and install software updates and patches, ensuring systems are always up-to-date and protected from vulnerabilities.
- System Monitoring: RMM solutions can continuously monitor system performance, resource utilization, and network traffic, alerting IT teams to potential issues before they escalate.
- Backup and Recovery: Automated backup and recovery procedures ensure data is protected and can be restored quickly in case of hardware failures or disasters.
- Endpoint Security: RMM tools can automatically enforce security policies, install antivirus software, and monitor for suspicious activity, enhancing endpoint security.
- Remote Access and Support: RMM solutions enable remote access to endpoints, allowing IT teams to troubleshoot issues and provide support remotely, reducing downtime and travel costs.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning into RMM solutions is rapidly transforming the landscape of IT management.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict potential hardware failures, allowing IT teams to proactively schedule maintenance and prevent downtime.
- Automated Incident Response: Machine learning can detect and respond to security threats in real-time, automatically isolating infected systems and preventing further damage.
- Smart Automation: AI-powered RMM solutions can learn from user behavior and adapt automation workflows to optimize efficiency and improve user experience.
- Proactive Security: AI can analyze security data and identify potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited, enabling proactive security measures.
Security Considerations in RMM
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) platforms offer significant benefits for IT teams, but they also introduce new security challenges. RMM solutions collect and manage sensitive data, including system configurations, user credentials, and network information, making them attractive targets for malicious actors.
Security Implications of Using an RMM Platform
The use of an RMM platform inherently involves security considerations, as it grants remote access to managed devices. This access can be exploited by attackers if security measures are not implemented properly.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to an RMM platform can lead to data breaches, exposing sensitive information such as user credentials, network configurations, and system logs. This data can be used for identity theft, malicious attacks, or unauthorized access to critical systems.
- Malware Infection: Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the RMM platform or its connected devices to deploy malware. This can compromise the entire network and lead to data theft, system damage, and denial-of-service attacks.
- Ransomware Attacks: RMM platforms can be targeted by ransomware attacks, where attackers encrypt critical data and demand payment for its decryption. This can cripple operations and lead to significant financial losses.
Best Practices for Securing RMM Data
Securing RMM data is crucial for protecting sensitive information and mitigating potential threats. Implementing robust security practices can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use strong passwords and enable MFA for all user accounts, including administrative accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more authentication factors, such as a password and a code sent to their mobile device.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in the RMM platform and its connected devices. This includes checking for outdated software, misconfigured settings, and unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt all data stored and transmitted by the RMM platform, including user credentials, system logs, and configuration files. Encryption makes it difficult for attackers to access and decrypt sensitive data even if they gain unauthorized access to the platform.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control policies to limit user access to only the data and resources they need. This helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep the RMM platform and all connected devices up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. Software updates often include security fixes that address known vulnerabilities.
Role of RMM in Mitigating Security Threats
While RMM platforms can introduce security risks, they also play a vital role in mitigating security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Patching: RMM platforms can automatically scan for vulnerabilities in connected devices and apply security patches to address them. This helps prevent attackers from exploiting known vulnerabilities.
- Endpoint Security: RMM solutions can enforce endpoint security policies, such as disabling USB ports, restricting access to specific websites, and implementing anti-malware software. This helps protect devices from malware infections and other security threats.
- Real-Time Monitoring: RMM platforms can monitor devices and networks for suspicious activity in real-time, enabling IT teams to detect and respond to security threats quickly.
- Incident Response: RMM solutions can help streamline incident response by providing tools for isolating infected devices, restoring backups, and analyzing security logs.
Closure
In conclusion, RMM management is an essential component of modern IT infrastructure management. Its ability to streamline operations, enhance security, and improve efficiency makes it a valuable investment for businesses of all sizes. As technology continues to evolve, RMM solutions will continue to play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and resilience of IT systems.
RMM management is a critical aspect of any organization’s security posture. It’s essential to track changes and updates to your security configurations, and that’s where a version control system can be invaluable. By using a version control system, you can maintain a detailed history of changes, making it easier to roll back to previous configurations if necessary and ensure that your RMM solutions are always up-to-date and effective.
