Remote monitoring and management tools are revolutionizing the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure. These powerful solutions provide a centralized platform for monitoring and controlling devices, networks, and applications, all from a remote location. By leveraging the power of automation and real-time insights, RMM tools empower IT teams to optimize performance, enhance security, and streamline operations, ultimately leading to significant cost savings and increased productivity.
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where IT issues are detected and resolved before they even impact your business. With RMM tools, this vision becomes a reality. From proactive monitoring to automated patch management, these solutions provide a comprehensive suite of features designed to simplify IT management and ensure seamless business continuity.
Introduction to Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) Tools
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are software solutions that allow businesses to remotely monitor and manage their IT infrastructure, including computers, servers, and network devices. These tools provide centralized control over IT assets, enabling IT professionals to proactively identify and resolve issues, improve system performance, and enhance security.
Benefits of Using RMM Tools
RMM tools offer numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Increased Efficiency: RMM tools automate tasks, such as software updates and security patching, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Improved Security: By monitoring systems for vulnerabilities and threats, RMM tools help businesses stay ahead of potential security breaches and ensure data protection.
- Reduced Costs: RMM tools can help businesses save money by minimizing downtime, preventing costly hardware failures, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Enhanced Productivity: With RMM tools, businesses can ensure their IT infrastructure is running smoothly, minimizing disruptions and maximizing employee productivity.
- Improved Compliance: RMM tools help businesses meet compliance requirements by automating tasks such as data backups and security audits.
Common RMM Tool Features
RMM tools offer a wide range of features designed to streamline IT management. Some common features include:
- Remote Access: This feature allows IT professionals to remotely access and control devices, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other tasks without physically being present.
- Patch Management: RMM tools automate the process of installing security updates and software patches, ensuring systems are protected from vulnerabilities and threats.
- Asset Inventory: RMM tools provide a comprehensive inventory of all IT assets, including hardware, software, and network devices, enabling businesses to track and manage their IT resources effectively.
- Performance Monitoring: RMM tools monitor system performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space, enabling IT professionals to identify and resolve performance bottlenecks.
- Alerting and Reporting: RMM tools generate alerts when issues arise and provide detailed reports on system health, security events, and other important information.
- Security Monitoring: RMM tools monitor for security threats, such as malware and unauthorized access attempts, and provide real-time alerts and incident response capabilities.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: RMM tools automate data backup and disaster recovery processes, ensuring business continuity in the event of a system failure or data loss.
Key Features of RMM Tools: Remote Monitoring And Management Tools
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are essential for businesses of all sizes, providing a centralized platform for managing IT infrastructure and ensuring optimal performance. RMM tools empower IT teams to remotely monitor, manage, and troubleshoot devices, applications, and networks, enabling them to proactively address issues and improve overall IT efficiency.
Essential Features of a Comprehensive RMM Solution
A comprehensive RMM solution offers a wide range of features designed to streamline IT operations and enhance security. Key features include:
- Remote Access and Control: RMM tools provide secure remote access and control capabilities, allowing IT professionals to connect to and manage devices remotely. This enables them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other administrative tasks without physically being present at the device location.
- System Monitoring and Reporting: RMM tools continuously monitor system health, performance, and resource utilization. They generate detailed reports that provide insights into system performance, identify potential issues, and track trends over time. This data helps IT teams proactively address problems before they escalate and optimize system performance.
- Patch Management: Patch management is crucial for maintaining system security and preventing vulnerabilities. RMM tools automate the process of identifying, downloading, and applying software updates and security patches to all managed devices. This ensures that systems are up-to-date and protected against known vulnerabilities.
- Endpoint Security: RMM tools incorporate endpoint security features, including antivirus and anti-malware protection, firewall management, and intrusion detection. These features help safeguard devices from malware, unauthorized access, and other security threats.
- Asset Management: RMM tools provide comprehensive asset management capabilities, allowing IT teams to track hardware and software inventory, manage licenses, and monitor asset usage. This information helps optimize resource utilization and ensure compliance with software licensing agreements.
- Automated Task Scheduling: RMM tools enable IT teams to automate repetitive tasks, such as software deployments, system backups, and security scans. This frees up valuable time for IT professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Ticketing and Help Desk: Many RMM tools include integrated ticketing and help desk features, allowing users to submit support requests and track their progress. This provides a centralized platform for managing IT support and ensuring timely resolution of issues.
Security and Compliance Features
Security and compliance are paramount in today’s digital landscape. RMM tools play a crucial role in enhancing security and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Key security and compliance features include:
- Multi-factor Authentication: RMM tools should support multi-factor authentication (MFA), requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access. This adds an extra layer of security and protects against unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: All data transmitted between devices and the RMM platform should be encrypted using industry-standard protocols, such as TLS/SSL. This ensures that sensitive information is protected during transmission.
- Role-based Access Control: RMM tools should implement role-based access control (RBAC), allowing administrators to define different levels of access and permissions for users. This helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
- Auditing and Logging: RMM tools should provide detailed auditing and logging capabilities, tracking all user activities and system events. This information is essential for compliance purposes and incident investigation.
- Compliance Reporting: RMM tools should offer comprehensive compliance reporting, enabling organizations to demonstrate compliance with industry regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS.
Comparison of RMM Tool Features
| Feature | Tool A | Tool B | Tool C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | $X per month | $Y per month | $Z per month |
| Scalability | Scalable to thousands of devices | Scalable to hundreds of devices | Scalable to tens of devices |
| Integrations | Integrates with popular IT tools | Limited integrations | No integrations |
| Security Features | Multi-factor authentication, data encryption, role-based access control | Data encryption, role-based access control | Basic security features |
| Compliance Reporting | Comprehensive compliance reporting | Limited compliance reporting | No compliance reporting |
Benefits of Using RMM Tools
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools have revolutionized the way IT departments manage and support computer systems. These tools offer a wide range of benefits, streamlining IT operations, improving security, and ultimately saving businesses time and money.
Improving IT Efficiency and Productivity
RMM tools automate many manual tasks, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM tools can automatically scan systems for missing patches and vulnerabilities, and then apply the necessary updates, eliminating the need for manual patching and reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Remote System Monitoring: RMM tools provide real-time insights into the health and performance of devices, allowing IT teams to proactively identify and address issues before they impact users. This helps prevent downtime and ensures smooth operations.
- Automated Task Scheduling: RMM tools allow IT professionals to schedule routine tasks, such as backups, software updates, and system maintenance, to be performed automatically, reducing the workload and minimizing human error.
Enhancing Security and Reducing Risks
RMM tools play a crucial role in bolstering security and mitigating risks by providing comprehensive protection against threats.
- Real-time Threat Detection: RMM tools constantly monitor systems for suspicious activity, detecting malware, ransomware, and other threats in real time. This allows for immediate response and minimizes the impact of attacks.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation: RMM tools conduct regular vulnerability assessments, identifying weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers. They also provide automated remediation options, patching vulnerabilities and securing systems against potential threats.
- Endpoint Security Management: RMM tools enable centralized management of endpoint security policies, ensuring consistent security measures across all devices. This helps maintain a high level of security and reduce the risk of breaches.
Saving Money and Resources
RMM tools help businesses save money and resources by streamlining IT operations, reducing downtime, and minimizing the need for on-site visits.
- Reduced Downtime: By proactively identifying and addressing issues, RMM tools minimize downtime, ensuring business continuity and reducing the financial impact of service disruptions.
- Lower IT Costs: Automating tasks and reducing the need for manual intervention, RMM tools help businesses save on IT labor costs. They also reduce the need for expensive on-site visits, further lowering expenses.
- Improved Resource Allocation: RMM tools provide valuable insights into system performance and resource utilization, allowing IT teams to optimize resource allocation and ensure efficient use of hardware and software.
Types of RMM Tools
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are categorized based on their functionality and the specific needs they address. Each type of RMM tool offers a unique set of features and benefits, allowing organizations to choose the best solution for their particular requirements.
Endpoint Management
Endpoint management RMM tools are designed to manage and secure devices within an organization’s network. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing various aspects of endpoints, including software updates, security patching, and device configuration.
- Software Updates and Patching: These tools automate the process of delivering software updates and security patches to endpoints, ensuring that systems are protected from vulnerabilities and operating efficiently.
- Device Configuration: Endpoint management RMM tools allow administrators to configure device settings, such as network access, security policies, and user permissions, from a central location.
- Inventory Management: These tools provide a comprehensive inventory of all endpoints within the network, including hardware and software details, making it easier to track and manage assets.
Examples of popular endpoint management RMM tools include:
- Datto RMM: Datto RMM is a comprehensive endpoint management solution that provides a wide range of features, including patch management, software deployment, and remote control.
- ConnectWise Automate: ConnectWise Automate is a powerful RMM tool that offers a robust set of features for managing endpoints, including scripting, automation, and reporting.
- N-able N-central: N-able N-central is a cloud-based RMM tool that provides a user-friendly interface for managing endpoints, including remote access, patch management, and security monitoring.
Network Monitoring
Network monitoring RMM tools focus on monitoring the performance and health of an organization’s network infrastructure. These tools provide real-time visibility into network traffic, device availability, and potential issues, enabling administrators to identify and resolve problems quickly.
- Network Performance Monitoring: Network monitoring RMM tools track key network metrics, such as bandwidth utilization, latency, and packet loss, to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize network performance.
- Device Availability Monitoring: These tools monitor the availability of network devices, such as servers, routers, and switches, ensuring that critical systems remain operational.
- Security Monitoring: Network monitoring RMM tools can detect suspicious network activity, such as intrusion attempts and malware infections, providing an early warning system for security threats.
Examples of popular network monitoring RMM tools include:
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM): SolarWinds NPM is a comprehensive network monitoring solution that provides deep insights into network performance, device health, and security threats.
- ManageEngine OpManager: ManageEngine OpManager is a network monitoring tool that offers a wide range of features, including performance monitoring, device discovery, and alert management.
- Auvik: Auvik is a cloud-based network monitoring solution that provides a user-friendly interface for managing network infrastructure, including device discovery, performance monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance RMM tools focus on protecting organizations from cyber threats and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. These tools provide a range of security features, including vulnerability scanning, endpoint protection, and data loss prevention.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Security and compliance RMM tools scan endpoints for vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for remediation, reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Endpoint Protection: These tools protect endpoints from malware, ransomware, and other threats, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
- Data Loss Prevention: Security and compliance RMM tools help organizations prevent sensitive data from leaving the network, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
Examples of popular security and compliance RMM tools include:
- Sophos Central: Sophos Central is a cloud-based security and compliance solution that provides a comprehensive suite of security features, including endpoint protection, vulnerability management, and data loss prevention.
- Trend Micro Worry-Free Services: Trend Micro Worry-Free Services is a security and compliance solution that offers a range of features, including endpoint protection, web security, and data encryption.
- Symantec Endpoint Protection: Symantec Endpoint Protection is a comprehensive endpoint security solution that provides protection against malware, ransomware, and other threats, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure.
Other Types of RMM Tools
In addition to endpoint management, network monitoring, and security and compliance, there are other types of RMM tools that address specific needs.
- Server Management: Server management RMM tools focus on managing and monitoring servers, providing features for server monitoring, patching, and backup.
- Help Desk and Ticketing: Help desk and ticketing RMM tools help organizations manage support requests and incidents, providing a centralized platform for tracking issues and resolving them efficiently.
- Cloud Management: Cloud management RMM tools provide a platform for managing cloud services, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, allowing organizations to monitor and manage their cloud resources effectively.
Choosing the Right RMM Tool

Selecting the right RMM tool is crucial for any organization looking to streamline IT management and enhance security. The right tool can significantly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and mitigate risks. However, with numerous RMM tools available, making the right choice can be overwhelming.
Key Factors to Consider, Remote monitoring and management tools
Choosing the right RMM tool requires careful consideration of several factors. These factors can be categorized into three main areas:
- Functionality: The RMM tool should offer the specific features you need to manage your IT infrastructure effectively. Consider the types of devices you need to manage, the level of automation you require, and the specific security features that are essential for your organization.
- Scalability: The RMM tool should be able to grow with your organization. Consider your current and future needs, including the number of devices you expect to manage and the potential for expansion.
- Integration: The RMM tool should seamlessly integrate with your existing IT systems and tools. This can help streamline workflows and reduce the need for manual data entry.
- Cost: RMM tools come with different pricing models. Consider your budget and choose a tool that offers the best value for your money.
- Support: The RMM tool provider should offer reliable customer support and documentation. This is essential for ensuring that you can resolve any issues that arise and get the most out of the tool.
Assessing Specific Business Needs
Before you start evaluating RMM tools, it’s essential to assess your specific business needs. This involves understanding your current IT infrastructure, your future goals, and the challenges you face.
- Identify your current IT infrastructure: Determine the types of devices you need to manage, including desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices.
- Define your future goals: Consider your IT goals, such as improving security, enhancing efficiency, or reducing costs.
- Identify your IT challenges: Analyze the specific challenges you face, such as managing security threats, maintaining compliance, or managing software updates.
Checklist of Questions to Ask Potential RMM Tool Vendors
Once you have a clear understanding of your business needs, you can start evaluating RMM tools. To ensure you are comparing apples to apples, use a consistent set of questions to evaluate each vendor.
- What features does your RMM tool offer? This will help you understand if the tool can meet your specific needs.
- How does your RMM tool integrate with my existing IT systems? This will help you assess the ease of implementation and potential for integration with your current tools.
- What is your pricing model? This will help you understand the cost of the tool and compare it to other vendors.
- What level of customer support do you offer? This will help you assess the vendor’s commitment to customer satisfaction.
- Can I access a free trial or demo? This will allow you to test the tool and see if it meets your needs before making a purchase.
Implementation and Deployment of RMM Tools
Implementing and deploying an RMM solution requires careful planning and execution. It’s crucial to consider the specific needs of your organization, the existing IT infrastructure, and the chosen RMM tool’s capabilities.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating an RMM tool with existing systems is essential for seamless operation and data flow. This integration can be achieved through various methods, including:
- API Integration: Most RMM tools offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that allow them to communicate with other systems. This enables data exchange and automation between the RMM tool and applications like ticketing systems, monitoring tools, or security platforms.
- Directory Services Integration: Integrating the RMM tool with Active Directory or LDAP can streamline user management and device provisioning. It allows for automatic user account creation and access control within the RMM tool based on existing directory data.
- Third-Party Integrations: Many RMM tools offer pre-built integrations with popular third-party applications, such as antivirus software, backup solutions, and network monitoring tools. This simplifies the integration process and provides a more unified IT management platform.
Training and Onboarding Users
Effective training and onboarding are crucial for ensuring successful RMM adoption. It’s essential to provide users with the necessary knowledge and skills to utilize the RMM tool effectively. This can be achieved through:
- Interactive Training Modules: Providing interactive online training modules allows users to learn at their own pace and access information on demand. These modules can cover various aspects of the RMM tool, including basic navigation, common tasks, and advanced features.
- Live Webinars and Demonstrations: Live webinars and demonstrations offer a more interactive learning experience, allowing users to ask questions and receive real-time guidance. This format is particularly effective for showcasing key features and functionalities.
- User Guides and Documentation: Comprehensive user guides and documentation are essential resources for users to reference when they need to perform specific tasks or troubleshoot issues. These materials should be easily accessible and regularly updated.
Security Considerations with RMM Tools
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are powerful assets for IT professionals, offering centralized control and visibility over systems and networks. However, these tools also present security risks that must be addressed to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of managed systems.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption and access controls are fundamental security measures for RMM tools. These measures safeguard sensitive information, including system configurations, user credentials, and network traffic, from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- Data Encryption: RMM tools should encrypt all data transmitted between the management console and managed devices. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the appropriate decryption key. Encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with strong key lengths are recommended for robust protection.
- Access Controls: Implement robust access controls to limit who can access the RMM tool and what actions they can perform. This includes assigning roles and permissions based on job responsibilities. For example, technicians might have access to specific devices or functions, while administrators have broader access rights. Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification, such as a password and a code generated by a mobile app.
Best Practices for Securing RMM Tools and User Data
Securing RMM tools and user data requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various best practices.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are effective. This includes scanning for known vulnerabilities, checking for misconfigurations, and evaluating the effectiveness of access controls.
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Encourage users to create strong, unique passwords for their RMM accounts. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification, such as a password and a code generated by a mobile app.
- Secure Communication Channels: Use secure communication channels like HTTPS to encrypt data transmitted between the RMM console and managed devices. Ensure that all communication is protected by strong encryption algorithms and protocols.
- Regular Software Updates: Regularly update the RMM tool and its components to patch vulnerabilities and implement security enhancements. Software vendors often release security updates to address known vulnerabilities, so staying up-to-date is crucial.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate the RMM server and its associated infrastructure from the rest of the network to limit the impact of a potential breach. This can help prevent attackers from gaining access to other systems or data.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implement robust data backup and recovery procedures to ensure that critical data is protected even in the event of a security incident. Regular backups allow you to restore data if it is lost or corrupted.
- User Awareness Training: Train users on security best practices, such as strong password creation, phishing awareness, and how to identify suspicious emails or websites. User education is essential to prevent social engineering attacks and other security threats.
Future Trends in RMM
The realm of remote monitoring and management (RMM) is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting user demands. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses and IT professionals to optimize their RMM strategies and leverage the full potential of these tools.
Impact of Cloud Computing and Mobile Devices
Cloud computing and mobile devices have profoundly impacted the RMM landscape, leading to a surge in remote workforces and the need for secure and scalable management solutions.
- Increased Remote Access: The rise of cloud computing has enabled businesses to access and manage their IT infrastructure remotely, making RMM tools more essential than ever.
- Mobile Device Management: The proliferation of mobile devices used for work requires robust RMM tools that can effectively manage and secure these devices.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-based RMM solutions offer unparalleled scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt to changing needs and easily scale their IT operations.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in RMM
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing RMM by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and providing valuable insights.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered RMM tools can analyze historical data and identify potential issues before they arise, minimizing downtime and proactive maintenance.
- Automated Remediation: AI-powered RMM tools can automatically identify and resolve common IT issues, reducing the workload on IT staff and freeing them to focus on more complex tasks.
- Security Threat Detection: AI-powered RMM tools can analyze network traffic and identify suspicious activity, providing early warnings of potential security breaches.
Integration with Other IT Tools
RMM tools are increasingly integrating with other IT tools and services, creating a more comprehensive and streamlined IT management experience.
- IT Service Management (ITSM): Integrating RMM tools with ITSM platforms can streamline incident management, improve communication, and enhance overall IT service delivery.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Integrating RMM tools with SIEM solutions can provide a unified view of security threats and incidents, facilitating faster detection and response.
- Cloud Management Platforms: RMM tools are increasingly integrating with cloud management platforms, simplifying the management of cloud-based infrastructure and applications.
Case Studies of RMM Tool Success
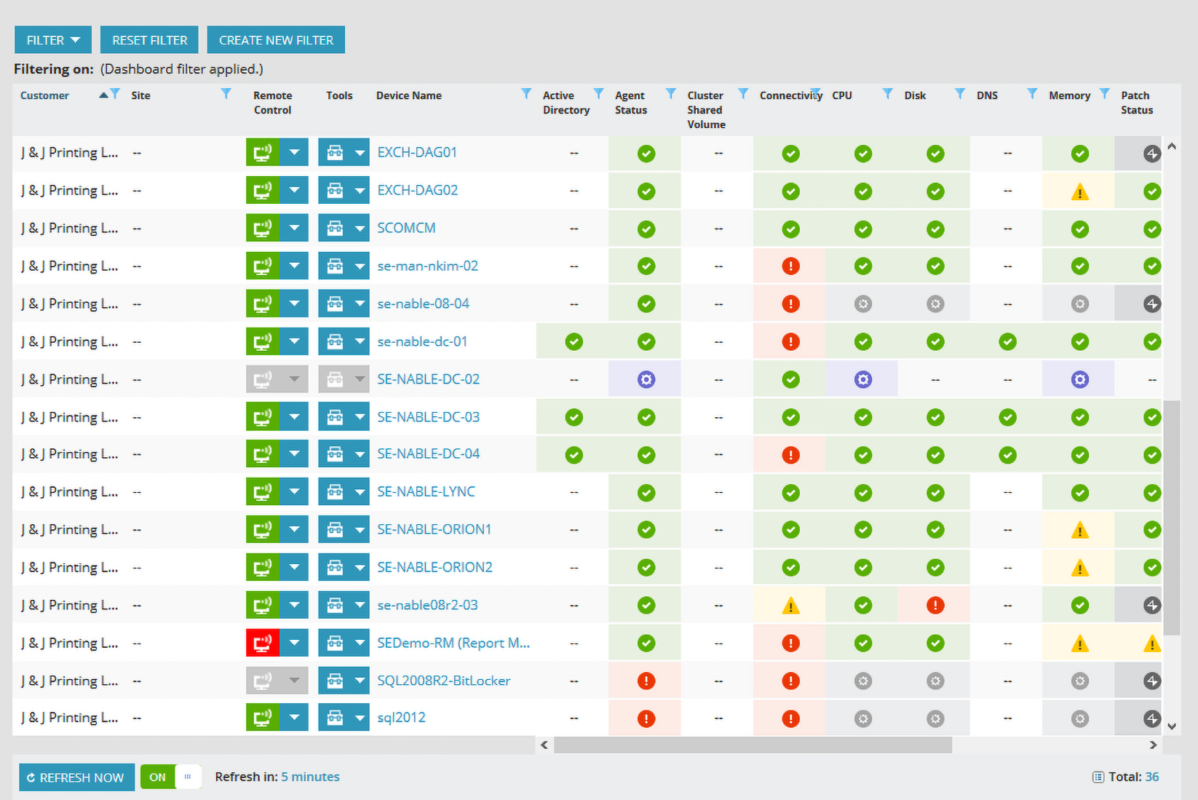
Real-world examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of implementing RMM tools. These case studies showcase how businesses have overcome challenges, achieved success, and realized significant returns on their investments.
Success Stories in Various Industries
RMM tools have proven effective across various industries, offering solutions tailored to specific needs.
- A healthcare provider, facing increasing compliance regulations and cybersecurity threats, adopted an RMM solution to automate patch management, vulnerability scanning, and endpoint security. This enabled them to ensure HIPAA compliance, minimize downtime, and reduce the risk of data breaches. The RMM tool allowed them to manage their IT infrastructure efficiently, freeing up valuable resources for patient care.
- A retail chain with numerous physical locations implemented an RMM tool to remotely monitor and manage their point-of-sale systems. This enabled them to proactively address performance issues, minimize downtime, and improve customer service. The RMM tool provided real-time insights into system performance, allowing them to identify and resolve problems before they impacted customers.
- A software development company leveraged an RMM tool to streamline their software development process and improve collaboration. The RMM tool enabled them to remotely access and manage their development environments, track progress, and collaborate effectively. This resulted in increased productivity, faster time-to-market, and reduced development costs.
Overcoming Challenges and Achieving Success
The implementation of RMM tools can present challenges, but with careful planning and execution, businesses can achieve significant success.
- A manufacturing company initially struggled with the integration of their existing IT infrastructure with the new RMM tool. They overcame this challenge by working closely with the RMM vendor and their internal IT team to develop a seamless integration strategy. This involved mapping existing systems and processes to the RMM tool’s capabilities, ensuring a smooth transition and minimal disruption to operations.
- A financial services firm faced resistance from employees who were hesitant to adopt the new RMM tool. They addressed this challenge by providing comprehensive training and support to employees, demonstrating the benefits of the tool and addressing their concerns. The firm also implemented a phased rollout approach, introducing the tool gradually and providing ongoing support to ensure user adoption.
- A non-profit organization encountered budget constraints during the implementation of an RMM tool. They addressed this challenge by carefully evaluating the various RMM solutions available and selecting a cost-effective option that met their specific needs. They also negotiated favorable terms with the vendor and implemented a phased rollout approach to manage costs effectively.
Measuring Return on Investment
The return on investment (ROI) for RMM solutions can be significant, but it’s essential to measure the benefits accurately.
- Reduced IT Costs: RMM tools automate many IT tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives. This can lead to significant cost savings by reducing the need for additional IT personnel.
- Improved Security: RMM tools enhance security by automating patch management, vulnerability scanning, and endpoint protection. This can reduce the risk of security breaches and minimize downtime, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Increased Productivity: RMM tools improve IT efficiency by automating routine tasks and providing real-time insights into system performance. This can lead to increased productivity and faster problem resolution, improving overall business operations.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: RMM tools help businesses provide faster and more efficient IT support, improving customer satisfaction. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
Analyzing Real-World ROI Examples
Real-world examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of RMM tools.
- A technology consulting firm implemented an RMM tool and reported a 20% reduction in IT support costs within the first year. This was achieved by automating routine tasks, reducing the need for on-site support, and improving the efficiency of IT operations.
- A healthcare provider using an RMM tool reported a 50% reduction in the number of security incidents. This was attributed to the tool’s automated patch management, vulnerability scanning, and endpoint protection capabilities.
- A manufacturing company implemented an RMM tool and reported a 15% increase in employee productivity. This was attributed to the tool’s ability to remotely access and manage workstations, improve collaboration, and streamline workflows.
Conclusion
In essence, remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools are a powerful solution for businesses of all sizes seeking to streamline IT operations, enhance security, and improve overall efficiency. By centralizing management tasks and automating routine processes, RMM tools empower IT professionals to proactively address potential issues before they escalate, ensuring optimal system performance and minimizing downtime.
Key Takeaways
The benefits of adopting RMM solutions are undeniable, encompassing enhanced security, reduced costs, improved efficiency, and increased visibility into IT infrastructure. RMM tools offer a comprehensive approach to managing IT environments, encompassing everything from remote access and software deployment to patch management and security updates.
Concluding Remarks
In today’s interconnected world, remote monitoring and management tools are no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses of all sizes. By embracing these powerful solutions, organizations can unlock a new level of efficiency, security, and scalability, ultimately paving the way for sustainable growth and success.
Remote monitoring and management tools are essential for businesses that operate remotely or have distributed teams. These tools allow administrators to monitor system performance, troubleshoot issues, and manage devices from anywhere in the world. One useful tool for remote communication and collaboration is Zoho Meeting , which provides secure video conferencing, screen sharing, and recording features.
These capabilities can be integrated into remote monitoring and management solutions to streamline communication and enhance collaboration among remote teams.
