Remote network administration tools have revolutionized the way we manage and maintain networks in today’s interconnected world. These powerful tools allow IT professionals to access and control network devices, monitor performance, troubleshoot issues, and implement security measures from any location with an internet connection.
Table of Contents
The ability to administer networks remotely has become increasingly crucial as businesses adopt hybrid and cloud-based infrastructure, requiring efficient management of geographically dispersed systems. Remote network administration tools provide a centralized platform for managing diverse network environments, simplifying tasks, reducing downtime, and improving overall IT efficiency.
Introduction to Remote Network Administration
Remote network administration refers to managing and controlling network devices and infrastructure from a remote location, often using specialized software tools and protocols. It has become increasingly important in modern IT environments due to the rise of cloud computing, distributed teams, and the need for 24/7 network availability.
Remote network administration offers several benefits, including increased flexibility, cost savings, and improved accessibility. However, it also presents unique challenges, such as security risks, latency issues, and the need for robust remote access solutions.
Challenges of Remote Network Administration
Managing networks remotely introduces several challenges that require careful consideration and appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Security Risks: Remote access opens up potential vulnerabilities for unauthorized access and data breaches. It’s crucial to implement strong authentication measures, secure network connections, and regular security audits to mitigate these risks.
- Latency: The distance between the administrator and the network devices can introduce latency, affecting the responsiveness of commands and potentially impacting network performance. This challenge can be addressed by optimizing network connections, using tools designed for remote administration, and implementing caching mechanisms.
- Accessibility Issues: Remote access may be limited by firewalls, network configurations, or other security measures. Administrators need to ensure they have the necessary permissions and access credentials to manage network devices remotely.
Scenarios Where Remote Network Administration is Essential
Remote network administration is essential in various scenarios, including:
- Managing Geographically Dispersed Offices: Organizations with offices in multiple locations need remote administration tools to manage their network infrastructure efficiently. This enables centralized control and monitoring of network devices across different geographical areas.
- Cloud Infrastructure Management: Cloud service providers rely heavily on remote network administration to manage their virtualized infrastructure, including servers, networks, and storage.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Remote access is critical for disaster recovery scenarios, allowing administrators to manage and restore network services from off-site locations.
Types of Remote Network Administration Tools
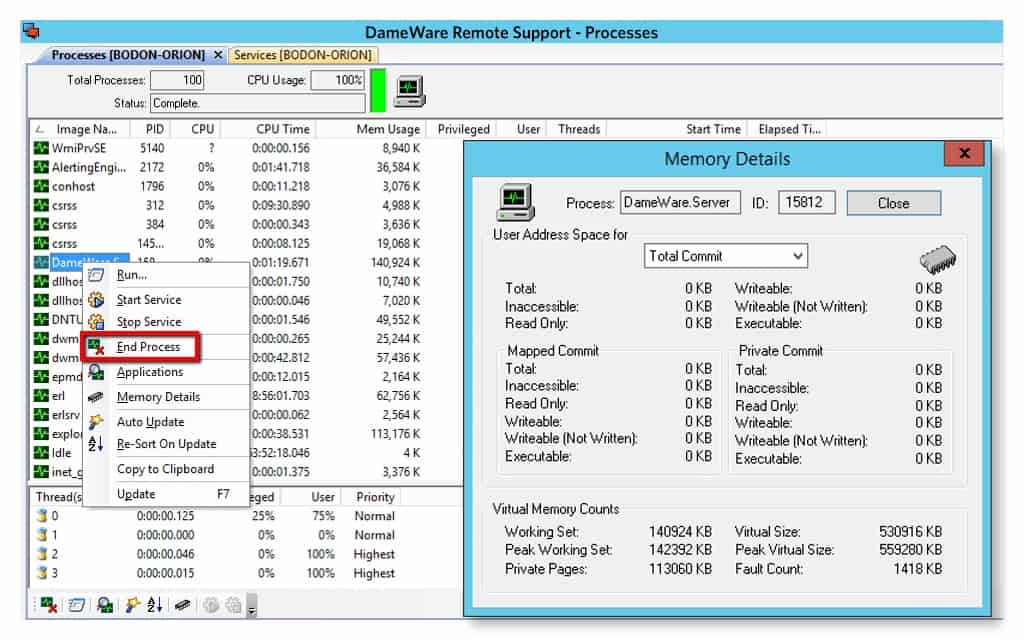
Remote network administration tools are essential for managing and maintaining networks from remote locations. These tools enable IT professionals to perform tasks such as monitoring network performance, configuring devices, troubleshooting issues, and securing the network infrastructure. Remote network administration tools can be categorized based on their functionalities, each category offering specific capabilities to address particular network management needs.
Remote Desktop Access
Remote desktop access tools allow administrators to control and manage remote computers as if they were physically present. These tools are crucial for troubleshooting, installing software, and providing technical support to users located remotely.
- Microsoft Remote Desktop: This popular tool offers secure remote access to Windows computers, enabling administrators to control the desktop, access files, and manage applications. Its strengths lie in its simplicity, compatibility with Windows operating systems, and integration with Active Directory. However, it requires a Windows server license and can be susceptible to security vulnerabilities if not configured properly.
- TeamViewer: TeamViewer is a versatile remote access solution that supports multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android. Its cross-platform compatibility and ease of use make it a popular choice for remote support and collaboration. However, its free version has limitations, and its paid versions can be expensive for large organizations.
- AnyDesk: AnyDesk is known for its fast performance and secure remote access capabilities. It supports various operating systems and provides features like file transfer, remote printing, and remote shutdown. Its strengths include its lightweight design, low latency, and high security standards. However, it lacks some advanced features compared to other solutions, such as remote control of mobile devices.
Network Management
Network management tools are designed to monitor and manage network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. These tools provide insights into network performance, identify potential issues, and allow administrators to configure and optimize network settings.
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM): NPM is a comprehensive network monitoring solution that offers real-time performance data, alerts for potential issues, and detailed network insights. It supports a wide range of network devices and provides comprehensive reporting capabilities. Its strengths include its user-friendly interface, advanced analytics, and robust reporting features. However, its pricing can be high, and it requires significant technical expertise to configure and maintain.
- ManageEngine OpManager: OpManager is another powerful network management tool that provides monitoring, reporting, and configuration capabilities. It supports various network devices, including routers, switches, servers, and applications. Its strengths include its comprehensive features, scalability, and support for multiple operating systems. However, its interface can be complex, and it may require specialized training for optimal utilization.
- PRTG Network Monitor: PRTG Network Monitor is a flexible and scalable network monitoring tool that offers real-time performance data, customizable dashboards, and comprehensive reporting. It supports a wide range of network devices and protocols, making it suitable for various network environments. Its strengths include its ease of use, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, its free version has limited features, and its paid versions can be expensive for large deployments.
Security Tools, Remote network administration tools
Security tools play a critical role in protecting networks from cyber threats. These tools help identify vulnerabilities, monitor network traffic, and implement security policies to mitigate risks.
- Cisco Secure Firewall: Cisco Secure Firewall is a robust and comprehensive firewall solution that provides advanced threat protection, network segmentation, and intrusion prevention. Its strengths include its scalability, performance, and integration with other Cisco security products. However, it can be complex to configure and requires specialized expertise.
- Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall: Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall is another powerful firewall solution that offers advanced threat detection, application control, and user-based security policies. Its strengths include its advanced security features, ease of management, and support for cloud environments. However, it can be expensive, and its deployment may require specialized expertise.
- Sophos XG Firewall: Sophos XG Firewall is a versatile firewall solution that provides comprehensive security features, including threat detection, intrusion prevention, and web filtering. Its strengths include its user-friendly interface, cost-effectiveness, and integration with other Sophos security products. However, it may not be as robust as other enterprise-grade firewall solutions.
Monitoring Solutions
Monitoring solutions are essential for ensuring network uptime and performance. These tools collect data from various network devices and provide insights into network health, identify potential issues, and enable proactive troubleshooting.
- Datadog: Datadog is a cloud-based monitoring platform that provides comprehensive insights into network performance, application health, and infrastructure metrics. Its strengths include its scalability, integration with various technologies, and user-friendly interface. However, its pricing can be high, and it requires a cloud-based infrastructure.
- New Relic: New Relic is another cloud-based monitoring platform that offers real-time performance data, detailed insights into application performance, and comprehensive reporting. Its strengths include its ease of use, integration with various technologies, and support for multiple operating systems. However, its free version has limited features, and its paid versions can be expensive for large deployments.
- Prometheus: Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system that provides real-time metrics collection, alerting, and visualization. Its strengths include its flexibility, scalability, and support for various data sources. However, it requires technical expertise to configure and maintain.
Device Management and Configuration

Remote network administration tools play a crucial role in managing network devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, and servers. These tools empower administrators to remotely configure, update, and troubleshoot network infrastructure, ensuring optimal performance and security.
Remote Configuration
Remote configuration tools enable administrators to make changes to network devices without physically accessing them. This is particularly valuable for geographically dispersed networks or devices located in remote or hazardous environments. These tools typically provide a graphical user interface (GUI) or a command-line interface (CLI) for configuring various device settings, including:
- IP addressing and routing
- Network security policies
- Quality of Service (QoS) settings
- VLAN configuration
- Wireless network settings
Firmware Updates
Network devices require regular firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities, enhance performance, and introduce new features. Remote network administration tools facilitate firmware updates, ensuring devices remain secure and up-to-date. These tools typically allow administrators to:
- Download the latest firmware from the vendor’s website
- Schedule firmware updates to minimize downtime
- Monitor the update process and receive notifications of completion or errors
Troubleshooting
Remote network administration tools provide valuable capabilities for troubleshooting network issues. These tools allow administrators to:
- View device logs and system information
- Monitor network traffic and performance metrics
- Run diagnostic tests and analyze network connectivity
- Remotely access device configuration and make necessary adjustments
Automation
Automation is a key aspect of device management, simplifying repetitive tasks and reducing the potential for human error. Remote network administration tools often offer automation features, allowing administrators to:
- Configure multiple devices simultaneously using scripts or templates
- Automate routine tasks such as firmware updates and security policy enforcement
- Implement proactive monitoring and alerting systems to detect and resolve issues before they impact network performance
For instance, a network administrator can use automation to configure a large number of switches with identical settings, ensuring consistency and reducing the time required for manual configuration. Similarly, automation can be used to schedule regular firmware updates for all network devices, minimizing downtime and ensuring that devices remain secure.
Ending Remarks
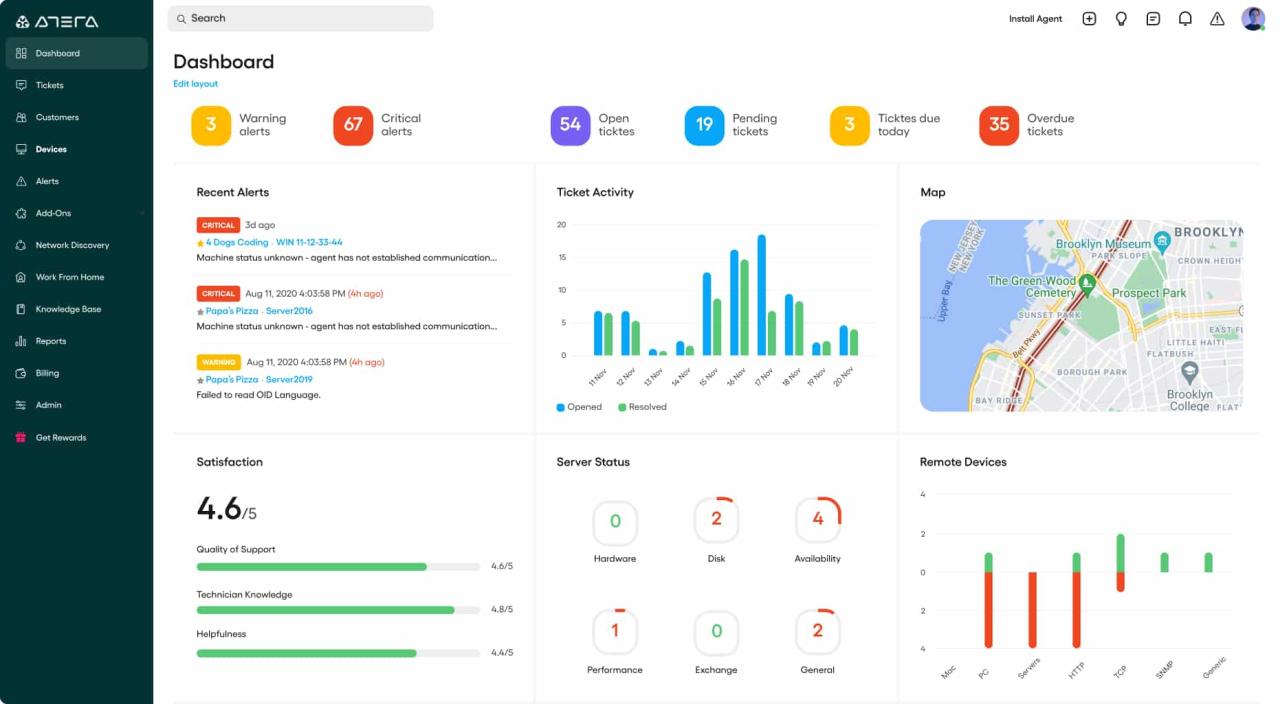
In conclusion, remote network administration tools have become indispensable for modern IT operations, empowering organizations to manage their networks effectively and securely from anywhere. By embracing these tools, businesses can optimize network performance, streamline operations, and enhance security posture, ultimately driving efficiency and productivity.
Remote network administration tools have evolved significantly over the years, offering a range of functionalities for managing and monitoring networks remotely. While tools like macromedia flash once dominated the web development landscape, they’ve been largely replaced by modern web technologies.
Today, remote network administration tools leverage these advancements to provide seamless and efficient network management, regardless of physical location.
