Remote tracking software sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of how technology empowers businesses and individuals to monitor and manage assets, resources, and even people. From fleet management to employee monitoring, this software has revolutionized how we track and analyze data in real-time, offering insights that can optimize operations, enhance safety, and improve efficiency.
Table of Contents
This guide delves into the intricacies of remote tracking software, exploring its functionalities, applications, and the crucial legal and ethical considerations surrounding its use. We’ll uncover the technical aspects of data collection, transmission, and analysis, as well as the diverse methods employed for tracking, including GPS, cellular networks, and Wi-Fi.
What is Remote Tracking Software?
Remote tracking software refers to applications and systems designed to monitor and track the location, activity, and status of assets, individuals, or vehicles remotely. This software leverages various technologies, such as GPS, cellular networks, and internet connectivity, to gather real-time data and provide insights into the tracked subjects.
Remote tracking software serves a multitude of purposes, ranging from enhancing security and safety to improving efficiency and productivity. It finds applications in various industries, including transportation, logistics, asset management, and personal safety.
Types of Remote Tracking Software
Remote tracking software encompasses a diverse range of applications catering to specific needs.
- GPS Tracking: GPS tracking software utilizes satellite signals to determine the precise location of vehicles, assets, or individuals. It is commonly used for fleet management, vehicle recovery, and personal safety.
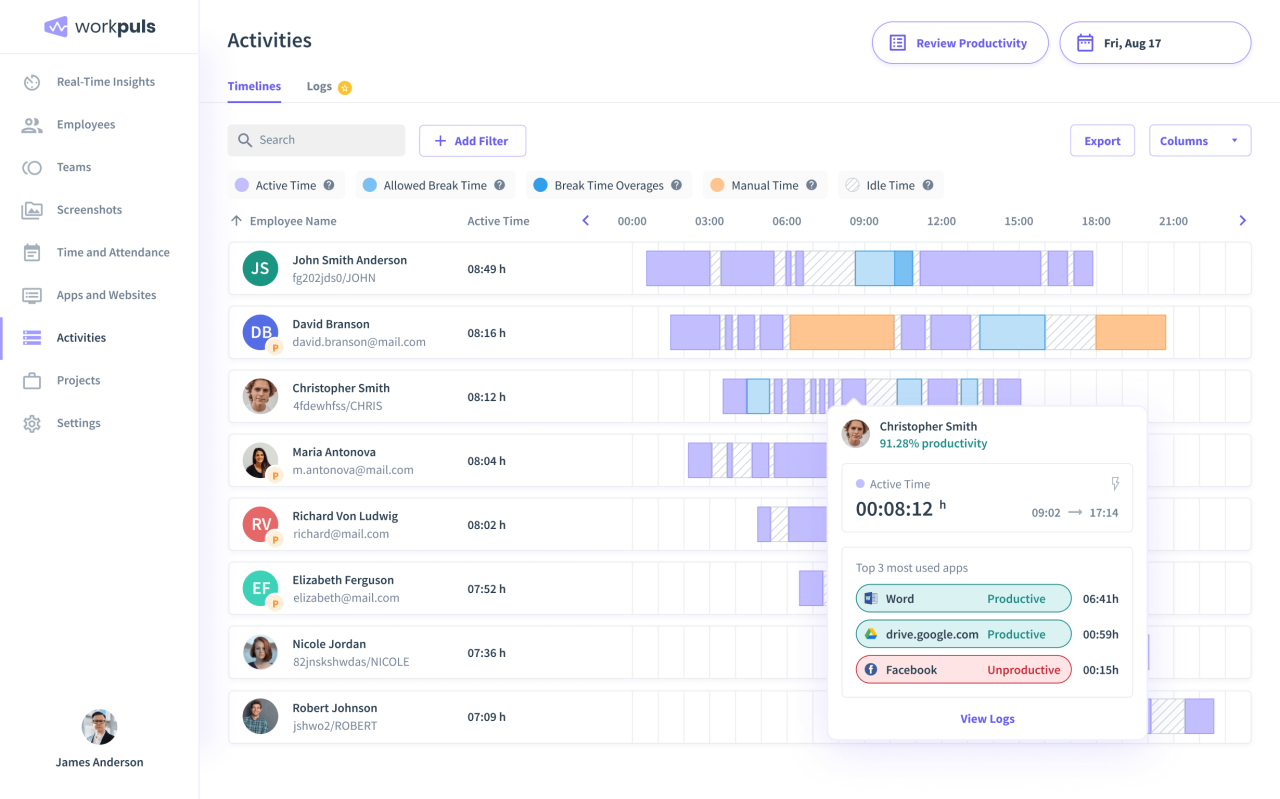
- Employee Monitoring Software: This type of software monitors employee activities on company-owned devices, such as computers and mobile phones. It can track internet usage, application access, and keystrokes, providing insights into employee productivity and compliance.
- Fleet Management Software: Fleet management software integrates GPS tracking with additional features like route optimization, fuel monitoring, and driver behavior analysis. It helps businesses optimize fleet operations, reduce fuel consumption, and improve driver safety.
Benefits of Using Remote Tracking Software
Remote tracking software offers a plethora of benefits across various industries.
- Enhanced Security: Remote tracking software can significantly enhance security by enabling real-time monitoring of assets, vehicles, and individuals. This can help prevent theft, vandalism, and other security threats.
- Improved Efficiency: By providing real-time insights into asset location and activity, remote tracking software helps optimize operations, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency.
- Increased Productivity: Employee monitoring software can provide valuable insights into employee productivity, identify areas for improvement, and optimize work processes.
- Cost Savings: Remote tracking software can help reduce operational costs by optimizing routes, minimizing fuel consumption, and improving asset utilization.
- Enhanced Safety: GPS tracking and driver behavior monitoring features can significantly improve safety by reducing speeding, harsh braking, and other risky driving behaviors.
Drawbacks of Using Remote Tracking Software
While remote tracking software offers numerous benefits, it also presents some potential drawbacks.
- Privacy Concerns: Employee monitoring software can raise privacy concerns, as it tracks employee activities on company-owned devices. It is essential to have clear policies and guidelines in place regarding employee monitoring.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining remote tracking software can be expensive, especially for large-scale deployments.
- Technical Issues: Remote tracking software relies on GPS signals and cellular networks, which can be susceptible to interference and outages.
- Misuse Potential: Remote tracking software can be misused for unethical purposes, such as tracking individuals without their consent or monitoring employee activities excessively.
Applications of Remote Tracking Software
Remote tracking software offers a wide range of applications across various industries, revolutionizing how businesses operate and manage their assets. By leveraging real-time data and insights, organizations can enhance efficiency, improve safety, and optimize their operations.
Industries and Applications of Remote Tracking Software
Remote tracking software has found its niche in various industries, each with unique requirements and benefits. Here’s a table outlining some key applications and their benefits:
| Application | Industry | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fleet Management | Transportation & Logistics | Real-time vehicle tracking, optimized routes, fuel efficiency, driver behavior monitoring, and improved safety. | Delivery companies like FedEx and UPS use remote tracking software to monitor their fleet, optimize delivery routes, and ensure timely deliveries. |
| Asset Tracking | Construction, Manufacturing, and Warehousing | Real-time asset location, inventory management, theft prevention, and improved asset utilization. | Construction companies use remote tracking software to monitor heavy equipment, ensuring efficient allocation and reducing downtime. |
| Employee Tracking | Field Service, Healthcare, and Security | Real-time location tracking, workforce management, improved response times, and enhanced safety. | Field service technicians can be tracked to ensure efficient scheduling and dispatch, while healthcare professionals can be located quickly in emergencies. |
| Patient Monitoring | Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring, early detection of health issues, improved patient outcomes, and reduced hospital readmissions. | Hospitals and clinics use remote tracking software to monitor patients’ vital signs, ensuring timely intervention and improved care. |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Remote tracking software offers a powerful tool for monitoring and managing various aspects of business and personal life. However, its use raises significant legal and ethical concerns that must be carefully considered.
Privacy and Consent
The use of remote tracking software raises significant privacy concerns. The software can collect a vast amount of personal data, including location, browsing history, keystrokes, and communication records. This data can be sensitive and must be handled responsibly to ensure individuals’ privacy is protected.
Obtaining explicit consent from individuals before tracking their activities is crucial. This consent should be informed, meaning individuals must be fully aware of what data will be collected, how it will be used, and for how long. It is also important to ensure that individuals have the right to withdraw their consent at any time.
Potential for Misuse and Abuse
While remote tracking software can be used for legitimate purposes, it can also be misused for unethical and illegal activities. For example, employers could use tracking software to monitor employees’ personal activities, violating their privacy.
A key concern is the potential for unauthorized access to tracked data. Hackers could exploit vulnerabilities in the software or network to gain access to sensitive information.
Data Security and Storage, Remote tracking software
The software developers and users must ensure that collected data is securely stored and protected from unauthorized access. This involves implementing robust security measures, such as encryption and access control mechanisms.
It is also essential to have clear policies and procedures for data retention and deletion. Data should only be stored for as long as necessary for the intended purpose and should be securely deleted when no longer required.
Implementation and Configuration

Remote tracking software implementation and configuration involve a series of steps that ensure proper setup and functionality. The process involves setting up tracking devices, configuring software accounts, and familiarizing oneself with the software’s features.
Setting up Tracking Devices
Setting up tracking devices is the first step in implementing remote tracking software. This process involves physically installing the devices and configuring them to communicate with the software.
- Device Selection: Choose a device compatible with the chosen software, considering factors like battery life, tracking accuracy, and desired features.
- Installation: Install the device according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring it’s placed securely in the target location.
- Activation: Activate the device by following the provided instructions, often involving entering a unique identifier or pairing it with the software account.
Configuring Software Accounts
Once the devices are set up, the next step is to configure the software accounts. This involves creating accounts, customizing settings, and configuring device permissions.
- Account Creation: Create a software account by providing necessary information, such as email address, password, and contact details.
- Device Linking: Link the tracking devices to the account by entering their unique identifiers or using the software’s pairing feature.
- Customization: Customize the software settings to match your specific requirements, such as tracking frequency, reporting intervals, and notification preferences.
- Permissions: Set permissions for each device, determining who has access to its tracking data and what actions they can perform.
Using the Software Effectively
After configuring the devices and accounts, it’s crucial to understand how to use the software effectively.
- Real-time Tracking: Utilize the software’s real-time tracking features to monitor the device’s location in real time.
- Historical Data: Access historical tracking data to view the device’s movement over specific time periods.
- Geofencing: Create virtual boundaries called geofences around designated areas. The software can notify you when a device enters or exits these boundaries.
- Reports: Generate reports to analyze tracking data, providing insights into device usage and movement patterns.
- Alerts: Configure alerts to receive notifications when specific events occur, such as exceeding speed limits, entering restricted areas, or device battery depletion.
Data Analysis and Reporting
![]()
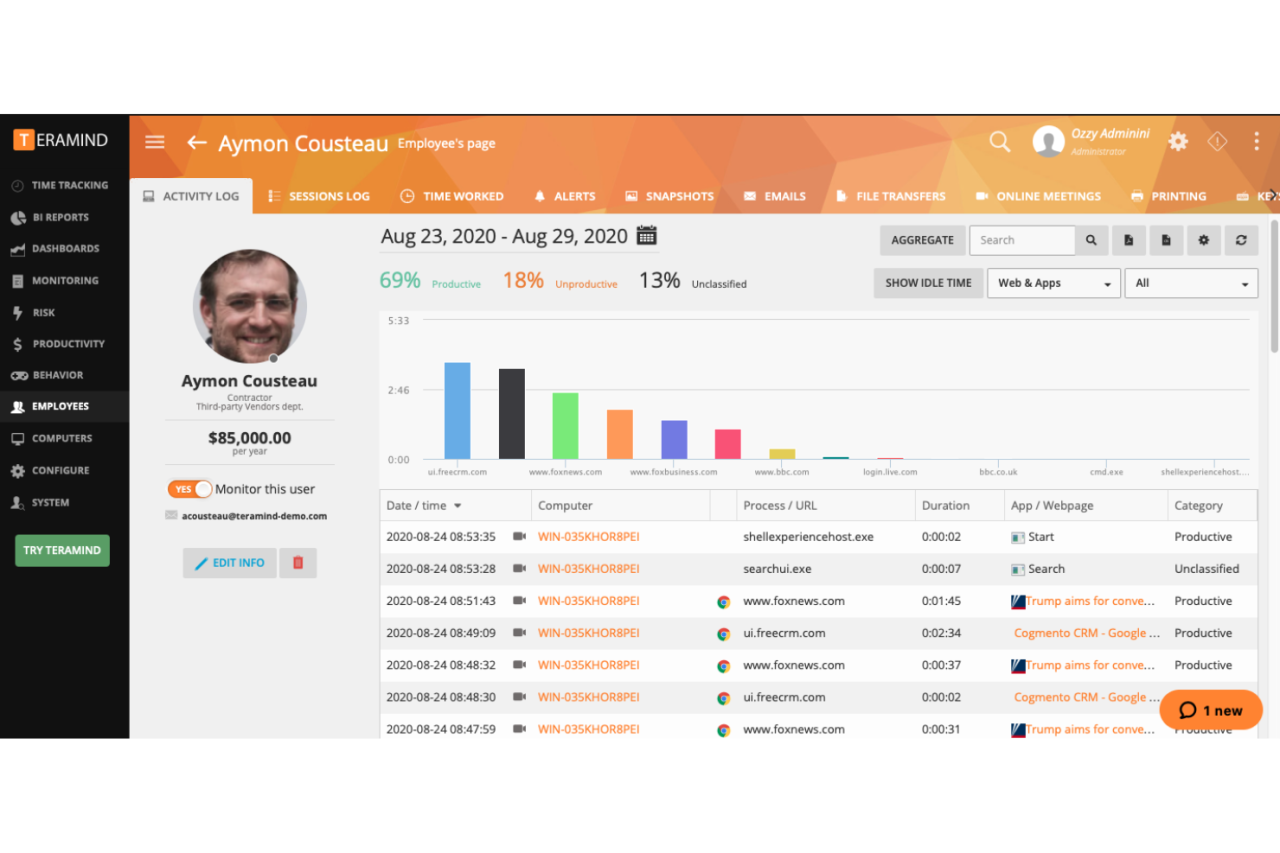
Remote tracking software collects a wealth of data that can be analyzed to gain valuable insights into various aspects of operations, employee performance, and asset utilization. Understanding how to analyze and interpret this data is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing processes.
Types of Data Collected
Remote tracking software gathers diverse data points that provide a comprehensive picture of activities and behaviors. This data can be categorized into several key types:
- Location Data: This includes GPS coordinates, timestamps, and addresses, providing real-time information about the location of tracked assets or individuals.
- Activity Data: This data captures information about the actions taken by tracked individuals or assets, such as speed, distance traveled, idle time, and work hours.
- Usage Data: This data provides insights into the utilization of tracked assets, including start and end times, frequency of use, and duration of use.
- Performance Data: This data measures the efficiency and productivity of tracked individuals or assets, including metrics like task completion rates, time spent on tasks, and overall performance scores.
- Environmental Data: This data includes information about the surrounding environment, such as temperature, humidity, and noise levels, which can be relevant for certain applications.
Data Analysis Methods
Analyzing remote tracking data involves applying various methods to extract meaningful insights and patterns. Common approaches include:
- Descriptive Analysis: This involves summarizing and describing the collected data using metrics like averages, medians, and standard deviations. This provides a basic understanding of the data’s characteristics.
- Trend Analysis: This method examines data over time to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies. This helps in understanding the evolution of behaviors and identifying potential issues.
- Correlation Analysis: This technique explores the relationships between different data points to determine if there are any connections or dependencies. This can help in identifying factors that influence performance or behavior.
- Predictive Analytics: This advanced method uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. This can help in anticipating potential problems and making proactive decisions.
Report Generation and Data Visualization
Effective data analysis requires clear and concise reporting to communicate insights to stakeholders. Data visualization plays a crucial role in making complex information easily understandable.
- Report Types: Reports can be tailored to specific needs and audiences, including summary reports, detailed reports, trend reports, and performance reports.
- Data Visualization Techniques: Various visualization tools and techniques can be used to present data effectively, including charts, graphs, maps, and dashboards. These tools can help in highlighting key trends, identifying outliers, and making comparisons.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): KPIs are specific metrics that measure the performance of tracked individuals or assets. These KPIs should be clearly defined and aligned with business goals.
Future Trends in Remote Tracking Software
The landscape of remote tracking software is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and other cutting-edge technologies. These innovations are paving the way for enhanced functionalities, broader applications, and a more intelligent approach to tracking and monitoring.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming the capabilities of remote tracking software by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and providing insightful data analysis. These technologies are enabling the software to learn from past data, identify patterns, and predict future events. For example, AI-powered algorithms can analyze GPS data to detect anomalies in vehicle behavior, such as sudden stops or excessive speeding, potentially indicating a safety concern or a potential security breach.
Enhanced Security and Privacy Features
As remote tracking software becomes more sophisticated, the importance of robust security and privacy features is paramount. Advanced encryption algorithms and multi-factor authentication are becoming increasingly common, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data.
Real-Time Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
Real-time data analytics is another key trend, allowing users to gain immediate insights from tracking data. By analyzing data streams in real-time, businesses can optimize operations, improve efficiency, and make proactive decisions. For example, predictive maintenance models can analyze sensor data from equipment to identify potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of remote tracking software with the Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding the scope of tracking capabilities. IoT devices, such as sensors, wearables, and smart devices, can be integrated with remote tracking platforms to provide real-time data on a wide range of parameters, including location, temperature, humidity, and more.
Cloud-Based Solutions and Scalability
Cloud-based remote tracking solutions are gaining popularity due to their scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud platforms enable users to access tracking data from anywhere with an internet connection, and they can easily scale their resources as needed.
Wrap-Up
As we navigate the evolving landscape of remote tracking software, it’s essential to embrace the technology’s potential while acknowledging the importance of responsible use. By understanding the benefits, drawbacks, and ethical implications, we can harness the power of remote tracking to enhance productivity, improve safety, and foster transparency in various sectors. The future holds exciting possibilities for this technology, with advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning poised to reshape how we track, analyze, and utilize data in the years to come.
Remote tracking software can be a powerful tool for businesses, but it’s important to consider the ethical implications. For example, if you’re looking to create a unique soundscape for your company’s marketing materials, you might want to explore the capabilities of virtual dj 7 download.
While this software can be a great resource for creative endeavors, it’s crucial to use remote tracking software responsibly and transparently, respecting the privacy of your employees and clients.