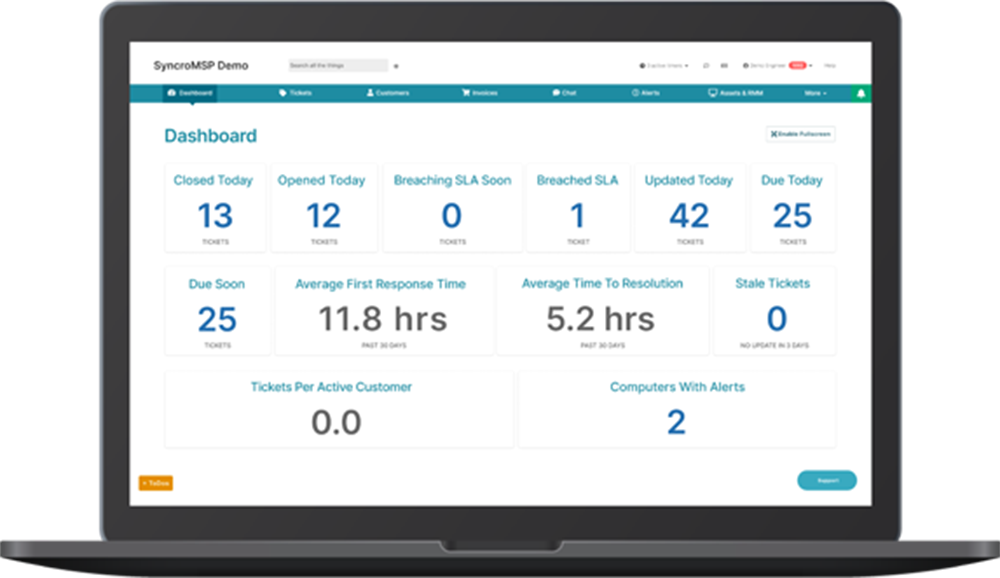
RMM MSP, a powerful combination of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solutions with Managed Service Provider (MSP) expertise, revolutionizes how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. By seamlessly integrating these technologies, MSPs gain the ability to remotely monitor, manage, and secure their clients’ systems, significantly enhancing efficiency and profitability.
Table of Contents
RMM solutions empower MSPs to automate tasks, proactively address issues, and ensure the highest levels of security for their clients. This streamlined approach not only reduces operational costs but also allows MSPs to focus on delivering high-quality services and building strong client relationships.
What is RMM?
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is a technology that allows IT professionals to remotely manage and monitor computer systems and networks. RMM solutions provide a centralized platform for managing IT infrastructure, including desktops, servers, and mobile devices.
Core Functionalities of RMM Solutions, Rmm msp
RMM solutions offer a wide range of functionalities designed to simplify and enhance IT management. Here are some of the key capabilities:
- Remote Access and Control: RMM solutions allow IT professionals to access and control devices remotely, enabling them to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other tasks without physically being present at the device location. This functionality is crucial for managing geographically dispersed systems or providing quick assistance to users experiencing problems.
- System Monitoring: RMM solutions continuously monitor various aspects of computer systems and networks, including CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network connectivity. They alert administrators to potential issues or performance bottlenecks, allowing them to proactively address problems before they impact users. This real-time monitoring helps prevent downtime and ensures optimal system performance.
- Patch Management: Keeping software up-to-date is essential for security and stability. RMM solutions automate patch management, ensuring that systems receive the latest security updates and bug fixes. This automated process reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and helps maintain a secure IT environment.
- Software Deployment: RMM solutions simplify software deployment by allowing administrators to push applications to multiple devices simultaneously. This streamlined process saves time and ensures that all systems have the necessary software for optimal operation. It also eliminates the need for manual installations on individual devices, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Backup and Recovery: Data loss can be catastrophic for businesses. RMM solutions provide backup and recovery capabilities, allowing administrators to create regular backups of critical data and restore systems in case of failures or data breaches. This ensures business continuity and minimizes downtime in the event of unexpected events.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM solutions generate detailed reports on system performance, security status, and other key metrics. These reports provide valuable insights into IT operations and help administrators identify areas for improvement. They also facilitate compliance reporting and demonstrate the effectiveness of IT management practices.
Real-World Examples of RMM in IT
RMM solutions are widely used in various IT scenarios, providing valuable benefits to organizations of all sizes. Here are some examples:
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs leverage RMM solutions to manage the IT infrastructure of their clients remotely. They can monitor systems, provide proactive maintenance, and respond to support requests efficiently, ensuring that clients’ IT operations run smoothly. RMM solutions are essential for MSPs to deliver high-quality services and maintain customer satisfaction.
- Large Enterprises: Large enterprises with geographically dispersed IT infrastructure benefit from RMM solutions for centralized management and control. They can monitor systems across multiple locations, ensure consistent security policies, and streamline software deployments, improving efficiency and reducing IT costs.
- Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs): SMBs often lack dedicated IT staff, making RMM solutions a valuable asset. They can automate tasks, monitor systems, and provide remote support, allowing SMBs to manage their IT infrastructure effectively without significant investments in IT personnel.
What is an MSP?
An MSP, or Managed Service Provider, is a company that provides IT services to other businesses on a managed basis. Instead of hiring an in-house IT staff, companies can outsource their IT needs to an MSP, who will manage their IT infrastructure and systems.
MSP Services
MSPs offer a wide range of services, which can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each client. Here are some common services offered by MSPs:
- Network Management: This includes managing the client’s network infrastructure, including routers, switches, firewalls, and other network devices. MSPs can help with network security, performance optimization, and troubleshooting.
- Server Management: MSPs can manage the client’s servers, including physical servers, virtual servers, and cloud servers. This includes tasks like server maintenance, security updates, backups, and disaster recovery.
- Desktop Support: MSPs can provide desktop support to users, including troubleshooting software issues, installing software, and providing technical assistance. This can be done remotely or on-site.
- Security Services: MSPs can help clients protect their IT infrastructure from cyber threats. This includes services like threat monitoring, intrusion detection, and data security.
- Cloud Services: MSPs can help clients migrate to the cloud, manage their cloud infrastructure, and provide cloud-based services. This can include services like cloud storage, cloud applications, and cloud security.
MSP Business Models
There are different business models that MSPs use to deliver their services. Some common models include:
- Fixed-Fee Model: This model involves a fixed monthly fee for a set of services. This can be a good option for businesses with predictable IT needs.
- Pay-Per-Use Model: This model charges for services on an as-needed basis. This can be a good option for businesses with unpredictable IT needs or those that only need occasional support.
- Project-Based Model: This model involves charging for specific IT projects, such as network upgrades or software implementations. This can be a good option for businesses that need help with one-time projects.
How RMM Benefits MSPs
RMM solutions are designed to streamline MSP operations, enhance security, and improve profitability. By automating tasks, centralizing management, and providing real-time insights, RMM empowers MSPs to deliver exceptional services and achieve greater success.
Increased Efficiency
RMM solutions significantly improve MSP efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, centralizing management, and providing real-time visibility into client systems.
- Automated Patching and Updates: RMM tools automatically deploy patches and updates to client systems, eliminating manual intervention and ensuring systems are secure and up-to-date.
- Remote System Monitoring: MSPs can monitor client systems remotely, proactively identifying and resolving issues before they impact users. This reduces the need for on-site visits and minimizes downtime.
- Centralized Management: RMM platforms provide a single console for managing all client systems, simplifying tasks and reducing administrative overhead. This centralized approach allows MSPs to easily track assets, monitor performance, and manage security policies.
- Automated Scripting and Task Execution: RMM tools allow MSPs to automate repetitive tasks, such as software installations, configuration changes, and data backups. This frees up valuable time for more complex and strategic initiatives.
Enhanced Security
RMM solutions play a crucial role in enhancing security for MSP clients by providing comprehensive endpoint protection, real-time threat detection, and automated security policy enforcement.
- Endpoint Security: RMM tools offer robust endpoint security features, including antivirus protection, firewall management, and intrusion detection systems. These features protect client systems from malware, ransomware, and other cyber threats.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Remediation: RMM platforms can scan client systems for vulnerabilities and automatically remediate them, reducing the risk of exploitation. This proactive approach helps MSPs stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: RMM solutions monitor client systems for suspicious activity and provide real-time alerts, allowing MSPs to quickly identify and respond to security incidents. This proactive approach helps minimize the impact of cyberattacks.
- Automated Security Policy Enforcement: RMM tools enforce security policies across client systems, ensuring consistent protection and reducing the risk of human error. This automated approach streamlines security management and improves compliance.
Improved Profitability
RMM solutions directly contribute to MSP profitability by reducing operational costs, increasing efficiency, and enabling MSPs to provide premium services.
- Reduced Operational Costs: RMM solutions automate tasks, reduce manual intervention, and minimize downtime, leading to significant cost savings for MSPs. This frees up resources for other revenue-generating activities.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: RMM tools empower MSPs to work more efficiently, allowing them to manage a larger number of clients with fewer resources. This increased productivity translates into higher revenue and improved profitability.
- Premium Service Offerings: RMM solutions enable MSPs to offer premium services, such as proactive monitoring, automated patching, and advanced security features. These services command higher margins and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Client Retention: By providing exceptional service and proactive security, RMM solutions help MSPs build strong client relationships and reduce churn. This improved client retention leads to a more stable revenue stream and increased profitability.
Key Features of RMM Solutions: Rmm Msp
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions are a vital tool for managed service providers (MSPs) to efficiently manage their clients’ IT infrastructure. RMM solutions offer a comprehensive suite of features that streamline operations, improve security, and enhance client satisfaction. This section explores the key features of RMM solutions and their impact on MSPs.
Remote Access
Remote access is a core feature of RMM solutions, allowing MSPs to connect to and manage client devices remotely. This capability eliminates the need for on-site visits, saving time and resources.
Advantages
- Reduced On-Site Visits: Remote access minimizes the need for physical visits, decreasing travel time and expenses.
- Faster Issue Resolution: MSPs can quickly diagnose and resolve issues remotely, reducing downtime and improving client satisfaction.
- Improved Efficiency: Remote access enables MSPs to manage multiple devices from a central location, enhancing overall efficiency.
Disadvantages
- Security Concerns: Remote access requires robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Connectivity Issues: Network connectivity issues can hinder remote access, delaying problem resolution.
- Limited Functionality: Some tasks may require physical access to the device, limiting the scope of remote management.
Patch Management
Patch management is crucial for maintaining system security and stability. RMM solutions automate patch deployment and ensure timely updates, reducing vulnerability to exploits.
Advantages
- Automated Updates: RMM solutions automate patch deployment, eliminating manual updates and reducing human error.
- Improved Security: Regular patching closes security vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of malware infections and data breaches.
- Enhanced System Stability: Patches often include bug fixes and performance improvements, contributing to system stability.
Disadvantages
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is a critical aspect of protecting client devices from malware and cyber threats. RMM solutions provide various endpoint security features, including antivirus, anti-malware, and intrusion detection.
Advantages
- Proactive Threat Protection: Endpoint security features detect and prevent malware attacks, protecting client devices from harm.
- Real-Time Monitoring: RMM solutions monitor endpoints for suspicious activity, enabling prompt threat response.
- Centralized Management: Endpoint security settings can be managed centrally, simplifying security administration.
Disadvantages
- Resource Consumption: Endpoint security software can consume system resources, impacting device performance.
- False Positives: Security software may sometimes flag legitimate programs as threats, leading to false positives.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM solutions generate comprehensive reports and analytics, providing valuable insights into IT infrastructure performance, security posture, and user activity.
Advantages
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Reports and analytics provide insights for informed decision-making regarding IT infrastructure optimization.
- Performance Monitoring: RMM solutions monitor system performance, identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Security Auditing: Reports provide evidence of security measures and compliance with industry standards.
Disadvantages
- Data Overload: Excessive data can be overwhelming and difficult to analyze.
- Reporting Complexity: Generating and interpreting reports can be complex, requiring specialized skills.
Other Key Features
RMM solutions offer a wide range of other features, including:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Software Inventory | Tracks installed software on client devices, enabling efficient license management and security audits. |
| Remote Scripting | Allows MSPs to execute scripts remotely, automating repetitive tasks and streamlining IT operations. |
| System Optimization | Provides tools for optimizing system performance, including disk cleanup, memory management, and process optimization. |
| User Management | Manages user accounts and permissions, enhancing security and streamlining user access. |
| Asset Management | Tracks hardware and software assets, simplifying inventory management and facilitating asset disposal. |
Selecting the Right RMM Solution
Choosing the right RMM solution is crucial for MSPs to streamline operations, enhance security, and improve client satisfaction. The decision involves careful consideration of various factors, including business needs, budget, and the specific features offered by different vendors.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an RMM Solution
- Business Needs: The first step is to identify your specific business needs and the challenges you want to address with an RMM solution. This includes determining the size and complexity of your client base, the types of devices you manage, and your security requirements.
- Budget: RMM solutions come with varying pricing models, from subscription-based to per-device fees. It is essential to establish a budget and explore solutions that align with your financial constraints.
- Features: Different RMM solutions offer diverse features, such as remote control, patch management, endpoint security, and reporting. Choose a solution that provides the features you need to manage your clients’ systems effectively.
- Ease of Use: The RMM solution should be user-friendly and easy to navigate, allowing your technicians to adopt it quickly and efficiently.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your RMM solution should be able to scale to accommodate the increasing number of clients and devices.
- Integration: Consider how well the RMM solution integrates with your existing IT tools and systems. Seamless integration can streamline workflows and reduce manual effort.
- Support: Choose a vendor that provides reliable technical support and documentation. Prompt and efficient support is essential for resolving issues and ensuring smooth operations.
Key Criteria for Evaluating RMM Vendors
- Reputation and Experience: Research the vendor’s reputation and experience in the RMM market. Look for vendors with a proven track record and positive customer reviews.
- Security: Ensure the vendor prioritizes security and offers robust features to protect client data. Look for certifications and compliance with industry standards.
- Features and Functionality: Evaluate the RMM solution’s features and functionality to ensure they meet your business needs and provide the capabilities you require.
- Pricing and Licensing: Compare pricing models, licensing options, and overall cost of ownership to find a solution that fits your budget.
- Customer Support: Assess the vendor’s customer support offerings, including response times, availability, and the quality of support provided.
Decision-Making Process Flowchart
- Identify Business Needs: Define the specific challenges and goals you want to address with an RMM solution.
- Set Budget Constraints: Establish a budget and explore solutions that align with your financial resources.
- Research and Compare Vendors: Identify potential vendors, research their reputations, and compare their offerings.
- Evaluate Features and Functionality: Analyze the features and functionality of each RMM solution to determine if they meet your requirements.
- Consider Ease of Use and Scalability: Assess the user-friendliness and scalability of the solution to ensure it can accommodate future growth.
- Evaluate Integration Capabilities: Determine how well the RMM solution integrates with your existing IT systems.
- Review Support and Documentation: Assess the vendor’s support offerings and documentation to ensure they meet your needs.
- Pilot Testing: Conduct a pilot test of the chosen solution to evaluate its performance and suitability for your environment.
- Final Decision: Based on the evaluation process, select the RMM solution that best aligns with your business needs and budget.
Implementing RMM in an MSP Environment
Implementing an RMM solution is a strategic move for MSPs, enabling them to effectively manage and monitor client systems remotely. The process involves a series of steps, from initial planning to ongoing optimization, ensuring a seamless transition and optimal performance.
Deploying an RMM Solution
Deploying an RMM solution requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and optimal performance. The following steps Artikel a comprehensive approach:
- Select an RMM Solution: The initial step involves choosing an RMM solution that aligns with the MSP’s specific needs and budget. This involves evaluating features, pricing, and compatibility with existing IT infrastructure.
- Install and Configure the RMM Agent: Once the solution is selected, the RMM agent needs to be installed on client endpoints. This involves deploying the agent through a variety of methods, such as software deployment tools or manual installation.
- Configure Security Settings: Security is paramount, and configuring the RMM agent’s security settings is crucial. This includes setting access control policies, encryption protocols, and authentication mechanisms to safeguard sensitive data.
- Define Monitoring Policies: Establishing monitoring policies is essential for proactive management. This involves defining the metrics to be monitored, frequency of checks, and thresholds for alerts.
- Integrate with Existing IT Infrastructure: Integrating the RMM solution with existing IT infrastructure is crucial for seamless operation. This may involve connecting to existing ticketing systems, active directories, or other tools.
- Train Staff: Training MSP staff on using the RMM solution is vital for efficient operation. This includes providing comprehensive training on the interface, features, and best practices for managing and monitoring systems.
Integrating RMM with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating the RMM solution with existing IT infrastructure is crucial for a seamless and efficient workflow. This involves connecting the RMM system with various tools and platforms used by the MSP, such as:
- Ticketing Systems: Integrating with ticketing systems allows for automatic incident creation and updates, streamlining the workflow and providing a centralized view of issues.
- Active Directory: Integrating with Active Directory enables the RMM solution to manage user accounts, permissions, and group policies, simplifying user management.
- Monitoring Tools: Integrating with monitoring tools provides a consolidated view of system performance, enabling MSPs to identify potential issues and proactively address them.
- Backup Solutions: Integrating with backup solutions allows for automated backup and recovery processes, ensuring data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
Managing and Monitoring RMM Systems
Effective management and monitoring of RMM systems are essential for optimal performance and security. Here are some best practices:
- Regularly Review and Update Security Settings: Security is an ongoing process, and it’s crucial to regularly review and update security settings to address evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
- Monitor System Performance and Resource Utilization: Monitoring system performance and resource utilization helps identify potential bottlenecks and optimize system efficiency.
- Proactively Address Alerts and Notifications: Promptly addressing alerts and notifications ensures timely resolution of issues, minimizing downtime and potential damage.
- Maintain Up-to-Date Software and Patches: Keeping software and patches up-to-date is crucial for security and stability, mitigating vulnerabilities and ensuring optimal performance.
- Regularly Back Up Configuration Data: Regularly backing up configuration data ensures data protection and allows for easy restoration in case of system failure or corruption.
RMM and Security

In today’s threat landscape, where cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, RMM solutions play a crucial role in protecting businesses and their valuable data. By proactively monitoring and managing endpoints, RMM tools empower MSPs to detect and respond to threats before they can cause significant damage.
Vulnerability Management
RMM solutions can significantly enhance vulnerability management by providing MSPs with the tools and insights needed to identify and address security weaknesses across their clients’ networks.
- Automated Patching: RMM tools can automatically deploy security patches to endpoints, ensuring that systems are updated with the latest security fixes. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM solutions often integrate with vulnerability scanning tools, allowing MSPs to regularly assess their clients’ networks for known security flaws. This provides a comprehensive overview of potential risks and enables proactive remediation.
- Prioritization and Reporting: RMM solutions help MSPs prioritize vulnerabilities based on severity and risk, allowing them to focus on the most critical issues first. They also provide detailed reports that document the identified vulnerabilities and the actions taken to address them.
Security Features Offered by RMM Solutions
RMM solutions offer a range of security features that help MSPs protect their clients’ networks from cyber threats. These features include:
- Antivirus and Endpoint Protection: Most RMM solutions integrate with leading antivirus and endpoint protection software, providing real-time threat detection and prevention. This helps safeguard endpoints from malware, ransomware, and other malicious attacks.
- Firewall Management: RMM tools allow MSPs to configure and manage firewalls on their clients’ networks, ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS): Some RMM solutions include IDS/IPS capabilities, which monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and block potential attacks. This provides an additional layer of security and helps detect and prevent advanced threats.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): RMM solutions can help MSPs implement DLP policies, preventing sensitive data from leaving their clients’ networks without authorization. This helps protect confidential information from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- User Access Control: RMM tools allow MSPs to control user access to systems and data, ensuring that only authorized personnel have the necessary privileges. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Security Auditing and Reporting: RMM solutions provide detailed security audit logs and reports, allowing MSPs to track security events, identify potential threats, and comply with industry regulations. This helps improve security posture and demonstrate compliance.
RMM and Automation
RMM solutions are not just about monitoring and managing devices. They are also powerful tools for automating tasks, which can significantly improve MSP efficiency and productivity. Automation streamlines repetitive processes, freeing up valuable time for MSPs to focus on higher-value tasks, such as strategic planning and client relationships.
Benefits of Automating Tasks with RMM
Automation with RMM offers numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Automating routine tasks eliminates manual intervention, allowing MSPs to complete tasks faster and with fewer errors.
- Reduced Costs: Automation minimizes the need for manual labor, leading to cost savings in terms of personnel time and resources.
- Improved Consistency: Automated tasks are performed consistently, ensuring adherence to best practices and reducing the risk of human error.
- Enhanced Security: Automation can help enforce security policies and patch vulnerabilities promptly, reducing the risk of cyberattacks.
- Improved Client Satisfaction: By delivering faster and more consistent service, automation can enhance client satisfaction and loyalty.
Common Tasks That Can Be Automated
Many common tasks performed by MSPs can be automated with RMM solutions:
- Patch Management: Automatically scan for and deploy software updates to ensure systems are secure and up-to-date.
- Backup and Recovery: Schedule and automate backups of critical data, ensuring data recovery in case of a disaster.
- Security Monitoring: Continuously monitor systems for suspicious activity and proactively respond to security threats.
- Remote Access: Automate remote access to client devices for troubleshooting and support, eliminating the need for on-site visits.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate automated reports on system performance, security events, and other relevant metrics.
- Ticket Management: Automate ticket creation, assignment, and escalation, streamlining the support process.
- Asset Management: Track and manage client hardware and software assets, ensuring inventory accuracy and compliance.
How Automation Improves MSP Productivity
Automation empowers MSPs to work smarter, not harder, by:
- Freeing Up Time: Automating repetitive tasks frees up MSP technicians to focus on more complex and strategic tasks.
- Improving Response Times: Automation allows MSPs to respond to client requests and incidents more quickly and efficiently.
- Enhancing Accuracy: Automation minimizes human error, ensuring tasks are completed accurately and consistently.
- Scaling Operations: Automation enables MSPs to scale their operations efficiently by handling increased workloads without adding significant staff.
- Increasing Profitability: By reducing costs and improving efficiency, automation can contribute to increased MSP profitability.
RMM and Reporting
Reporting is a critical component of any successful RMM strategy. It provides MSPs with valuable insights into the health and performance of their clients’ IT infrastructure, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
Types of RMM Reports
RMM solutions offer a wide range of reports that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of MSPs. These reports provide insights into various aspects of IT infrastructure, including:
- Device Inventory: This report provides a comprehensive list of all devices managed by the RMM solution, including hardware specifications, operating system versions, and software installations. This information is crucial for asset management, software licensing compliance, and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
- Patch Management: This report tracks the status of security patches across all managed devices. It helps MSPs identify devices that are missing critical updates and prioritize patching efforts to mitigate security risks.
- Security Posture: This report analyzes the security configuration of managed devices, identifying potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses. It helps MSPs proactively address security risks and improve the overall security posture of their clients’ networks.
- Performance Monitoring: This report tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk space. It helps MSPs identify performance bottlenecks and optimize system resources for improved efficiency and user experience.
- Help Desk Activity: This report provides insights into the volume and nature of support requests received from clients. It helps MSPs identify common issues, track service level agreements (SLAs), and optimize their support processes.
- Service Utilization: This report tracks the usage of different services offered by the MSP, such as backup, monitoring, and security. It helps MSPs identify popular services, optimize pricing models, and tailor service offerings to meet client needs.
- Financial Reports: These reports provide financial summaries of MSP operations, including revenue, expenses, and profitability. They help MSPs track their financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic business decisions.
Using Reports to Improve MSP Operations
RMM reports can be used to improve MSP operations in various ways:
- Proactive Maintenance: By analyzing reports on device inventory, patch management, and security posture, MSPs can identify potential issues and proactively address them before they become major problems. This reduces the risk of downtime, improves client satisfaction, and minimizes support costs.
- Optimize Service Delivery: Reports on help desk activity and service utilization can help MSPs identify common issues, optimize support processes, and tailor service offerings to meet client needs. This improves service efficiency, reduces support costs, and enhances client satisfaction.
- Improve Security: By monitoring security reports and proactively addressing vulnerabilities, MSPs can improve the security posture of their clients’ networks and reduce the risk of cyberattacks. This is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring business continuity.
- Make Informed Business Decisions: Financial reports provide valuable insights into MSP operations, enabling them to track profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic business decisions. This helps MSPs grow their business, increase revenue, and improve overall performance.
Final Conclusion
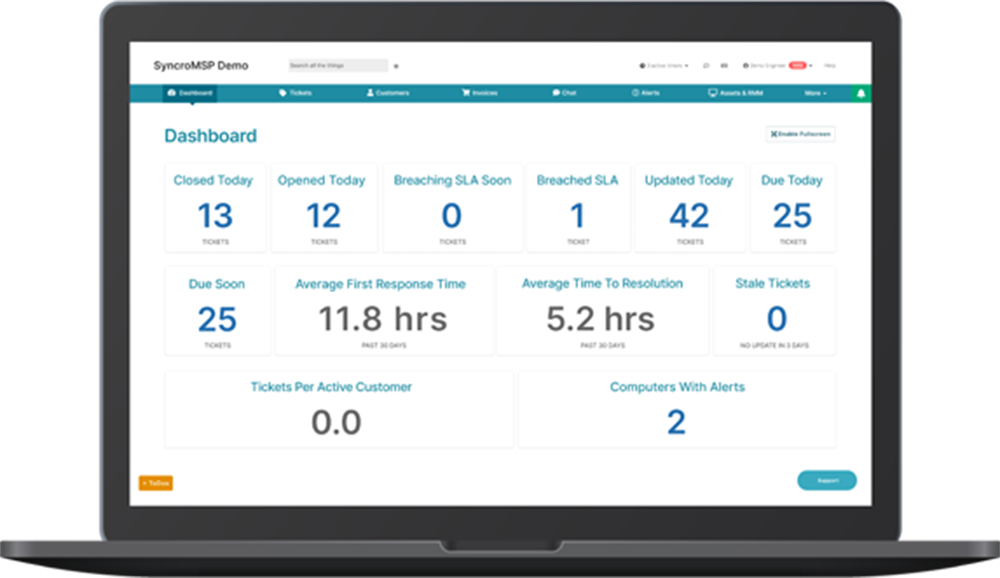
As technology continues to evolve, the importance of RMM MSP solutions will only grow. By embracing these powerful tools, MSPs can position themselves for success in the competitive IT landscape. Through automation, proactive maintenance, and enhanced security, RMM MSP solutions empower businesses to thrive in the digital age.
RMM MSPs are essential for managing IT infrastructure, but finding the right tools can be a challenge. One popular option for project management is freedcamp , which offers a comprehensive suite of features at an affordable price. This can be a valuable resource for RMM MSPs, allowing them to streamline workflows and improve communication with clients.